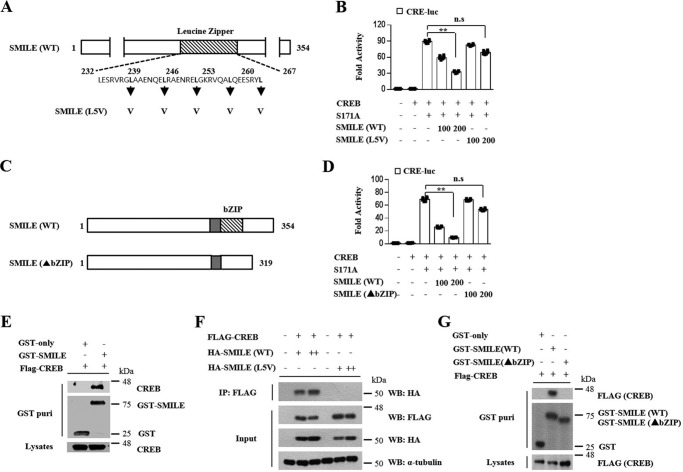
Figure 4.
Leucine zipper of SMILE is essential for inhibition of CREB/CRTC2 signaling. A, the basic region and leucine zipper domains of WT SMILE. The leucine zipper mutant SMILE (L5V) indicates the leucine residues between positions 239 and 267 were mutated to valine, as indicated by the arrows. B, AML12 cells were cotransfected with CRE-Luc, CREB, S171A, SMILE (WT), and SMILE (L5V). C, schematic representation of the truncated structures of the leucine zipper domains of SMILE (▴bZIP). D, AML12 cells were cotransfected with CRE-Luc, CREB, S171A, SMILE (WT), and SMILE (▴bZIP). E, 293T cells were cotransfected with expression vectors for FLAG-CREB with pEBG-SMILE (GST-SMILE) or pEBG alone (GST-only). Complex formation (upper two panels, GST purification) and the amount of FLAG-CREB (lower panel, lysate) used for the in vivo binding assay determined the interaction with the anti-FLAG antibody. F, 293T cells were cotransfected with expression vectors for HA-SMILE and FLAG-CREB. Co-immunoprecipitation assays were performed using cell extract from 293T cells using indicated antibodies. G, 293T cells were cotransfected with expression vectors for FLAG-CREB with WT SMILE expressing (WT) or leucine zipper domain truncated SMILE (▴bZIP). Complex formation (upper two panels, GST purification) and the amount of FLAG-CREB (lower panel, lysate) used for the in vivo binding assay. Error bars show mean ± S.D. n.s., not significant; **, p < 0.01 by two-tailed Student's t test. Results are representative of three independently performed experiments.