Figure 5.
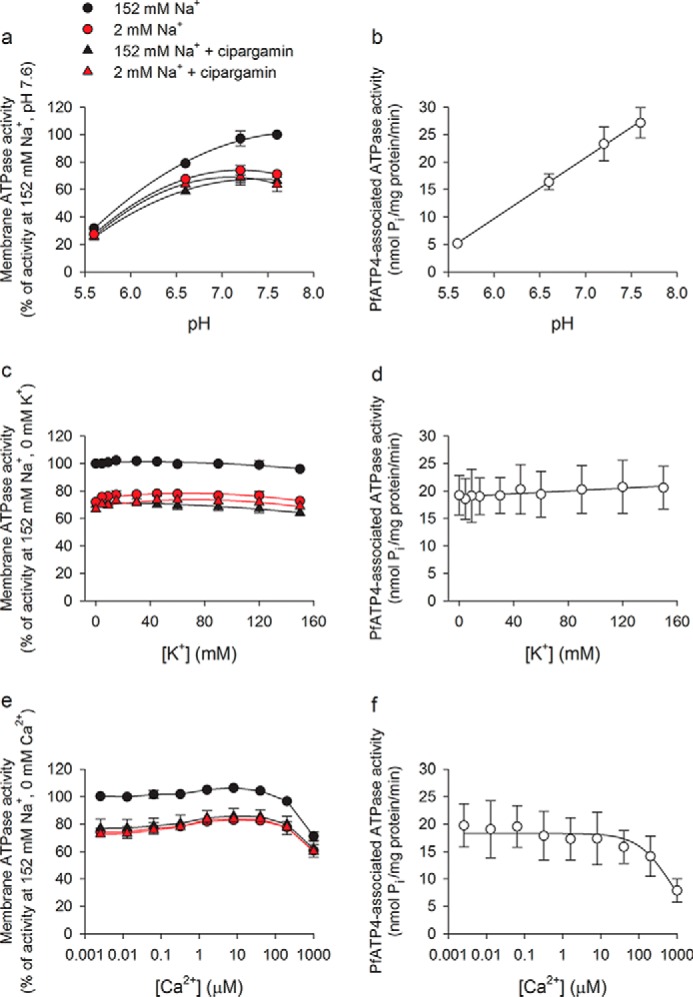
Effect of pH (a and b), [K+] (c and d), and [Ca2+] (e and f) on membrane ATPase activity and PfATP4-associated ATPase activity. Total ATPase activity (a, c, and e) was measured under high-[Na+] (black) and low-[Na+] (red) conditions and in the presence (triangles) and absence (circles) of cipargamin (500 nm). PfATP4-associated ATPase activity (b, d, and f) was calculated by subtracting the (pre-normalized) data obtained in the presence of cipargamin (and a high [Na+]) from those obtained in the high-[Na+] condition in the absence of cipargamin. The data were obtained with Dd2 parasites and are shown as the mean (± S.D.) from three independent experiments, each performed on different days with different membrane preparations. Where not shown, the error bars fall within the symbols. In the experiments in which [K+] was varied, [choline] was also varied such that [KCl] + [choline chloride] = 150 mm in the high-[Na+] condition. Choline was also used to replace Na+ in the low-[Na+] condition. e and f, [Ca2+] indicated corresponds to free [Ca2+] and was determined by adding 1 mm EGTA to the reaction mixture as well as sufficient CaCl2 to achieve the desired free [Ca2+] (Ca-EGTA Calculator v1.3).
