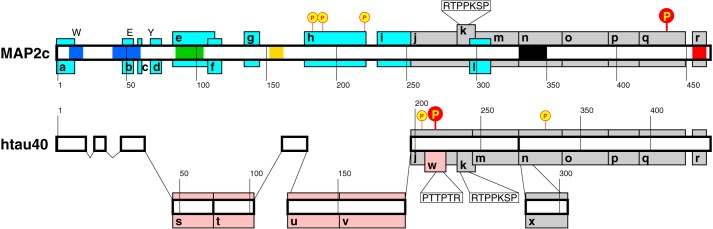
Figure 1.
Schematic drawing of the MAP2c and htau40 molecules. Regions associated with functions of MAP2c, htau40, and both proteins are shown as cyan, pink, and gray boxes, respectively, and labeled as follows. a–d, f, and l, proposed neurosteroid-binding site (57); e, RII site; g, proline-rich region coded by exon 7; h, proline-rich region coded by exon 14 and phosphorylated by PKA; i, short proline-rich region P1 of MAP2c; j, proline-rich region P2; k, Class I Fyn-binding site; m, MTBR1; n, MTBR3; o, MTBR4; p, region R′; q, region homologous to the muscarinic receptor binding site of Tau; r, C-terminal α-helix; s, near-N-terminal insert I1; t, near-N-terminal insert I2; u, region including α-helix 114LEDEAAGHVT123; v, long proline-rich region P1 of Tau; w, Class II Fyn-binding site; x, MTBR2. Regions of Tau with high homology with MAP2c are drawn closer to the scheme of MAP2c. Red and yellow circles, residues phosphorylated by PKA with high and medium rate, respectively (11, 13). SH3 recognition motifs are displayed in white boxes. Colored segments of the middle bar refer to clusters of spectral density values plotted in Fig. 7 (b and d). Positions of Trp14, Glu52, and Tyr67 of MAP2c are marked by W, E, and Y.