Figure 3. Inhibition of Autophagy during Activation Induces an Anergic State in Human T Cells.
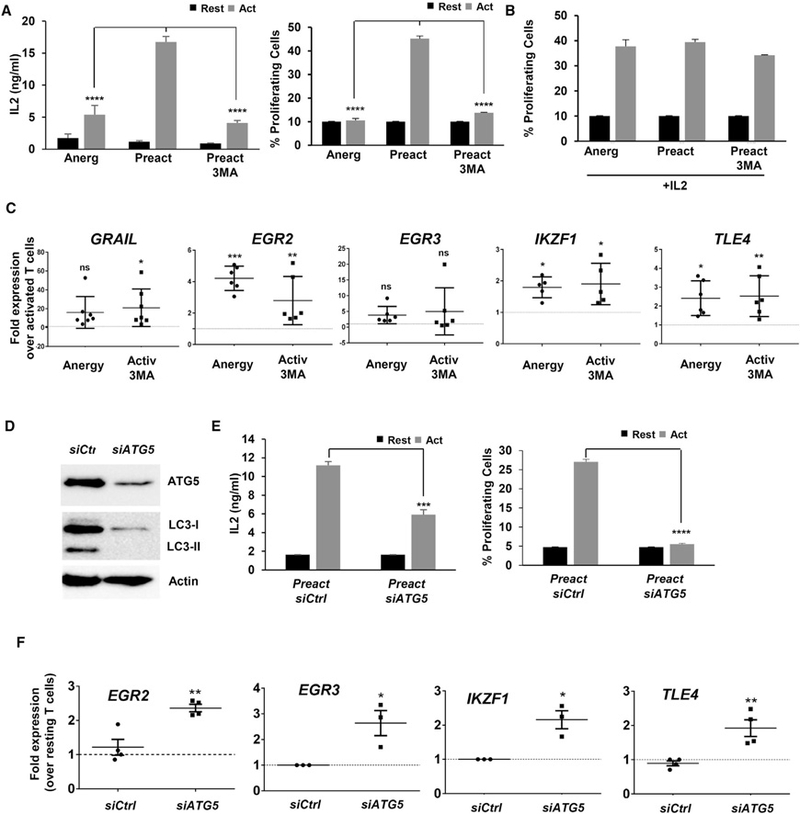
(A) Human CD4+ T cells were stimulated for 24 hr in the presence or absence of 3MA. Cells were washed to remove inhibitors and re-stimulated after 5 days. IL-2 production and cell proliferation were measured after 48 hr and 4 days, respectively. Data show mean + SEM of three experiments. ****p < 0.0001 (ANOVA).
(B) Human CD4+ T cells were activated in the presence or absence 3MA as in (A). After washing, cells were grown for 5 days with 50 ng/mL IL-2 and re-stimulated. Cell proliferation was measured.
(C) Expression of anergy-associated gene (qPCR) in human CD4+ T cells activated in the presence or absence of 3MA for 24 hr. B2M expression was used as normalization control. Values (mean ± SEM) from three experiments are expressed as fold increase relative to control cells activated in the absence of any inhibitor. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (ANOVA). ns, not significant.
(D and E) Human CD4+ T cells activated and transfected with either a non-targeting (Ctrl) or an ATG5-specific siRNA. (D) ATG5 and LC3 detected by immunoblot after activation 24 hr post-siRNA transfection. β-ACTIN was used as control. (E) IL-2 production and cell proliferation in cells re-stimulated 5 days after siRNA transfection. Data are mean + SEM of three experiments. ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001 (two-tailed t test).
(F) Expression of anergy-associated genes (qPCR) in control or ATG5 siRNA-transfected cells activated for 24 hr. B2M expression was used as normalization control. Values (mean ± SEM) of three different experiments are expressed as fold increase relative to control untransfected cells. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. Act, stimulated; Rest, resting.
