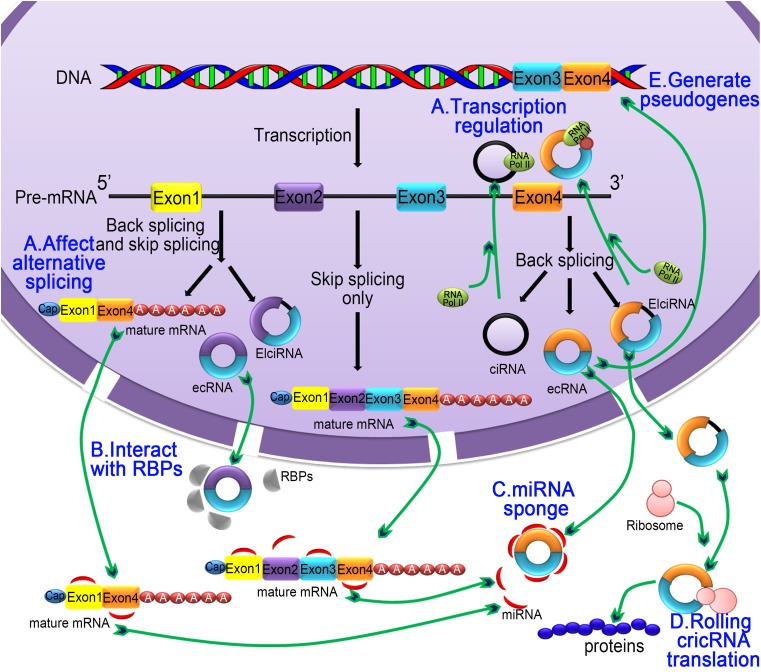
Figure 3. The five main functions of the circRNA.
(A) Regulating selective splicing or transcription: Stable circRNA and EIciRNAs are located in the nucleus, where they bind to RNA polymerase and promoting transcription; circRNA competes with pre-mRNA splicing to reduce the level of linear mRNA and excludes specificity from pre-mRNA by changing the composition of processed mRNA; (B) interaction with RBPs: circRNA binds with RBPs and ribonucleoprotein complexes and interfere with their functions. As a single circRNA can bind with multiple units of RBPs, they serve as stores of RBPs; (C) miRNA sponging activity: circRNA binds with miRNA and affecting the miRNA-dependent target gene suppression; (D) rolling circle translation: some circRNA can be translated into proteins by means of a roll loop amplification mechanism; (E) generation of pseudogenes: some circRNA are reverse transcribed into cDNA and integrated into the genome; however, the mechanism of integration is not yet clear.