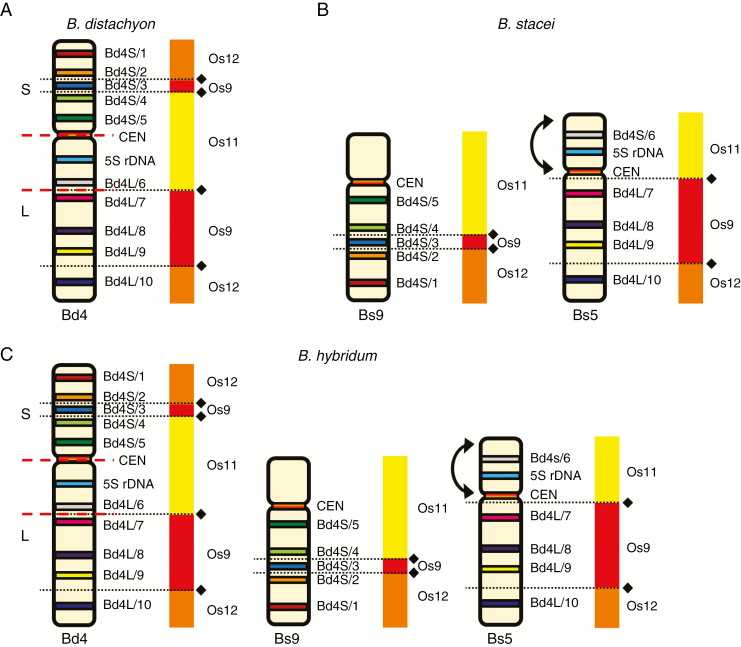
Fig. 7.
Chromosomal distribution of the BAC clones that were derived from chromosome Bd4 of B. distachyon (A) and comparatively mapped to the chromosomes of B. stacei (B) and B. hybridum (C). The distribution of the clones on the chromosome diagram (A) reflects their position on the physical map of the B. distachyon genome (Febrer et al., 2010). The diagrams next to the Brachypodium chromosomes relate the BAC clones to homoeologous regions in different rice chromosome equivalents. Black diamonds and dotted lines indicate the hypothetical fusion points of the intermediate ancestral grass chromosomes in Bd4 (adapted from IBI, 2010). Red dashed lines indicate the chromosomal breakpoints that were found in the Bs-genome chromosomes in B. stacei and B. hybridum. Arrows point to the inversion that was present on chromosomes Bs5 of these species.