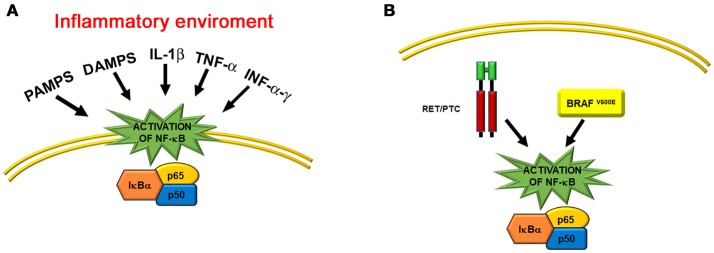
Figure 3.
Schematic representations of the two main mechanisms that activate NF-κB in thyroid cells. (A) Activation of the NF-κB pathway in an inflammatory environment, such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Some of the main factors that act throughout transmembrane and cytosolic receptors are indicated. (B) Activation of the NF-κB pathway by thyroid oncogenes, such as the cytosolic RET/PTC rearranged protein and the cytosolic BRAFV600E mutated kinase.