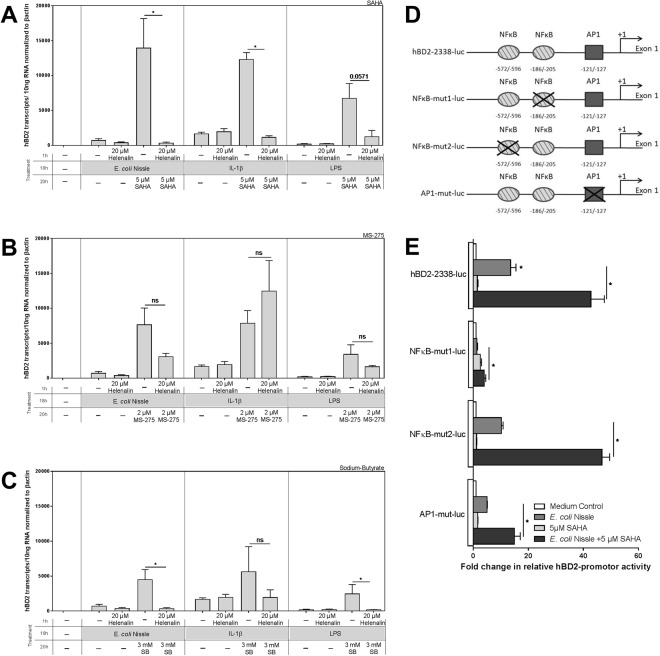
Figure 4.
Pan-histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition enhancement of human β-defensin 2 (hBD2) expression is dependent on nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB). (A–C) Show the abolishment of the enhancing effect of HDAC inhibition through Helenalin in CaCo-2/TC7 cells. HBD2 mRNA induction in response to EcN (3 × 108 CFU/ml), IL1β (10 ng/ml) or LPS (1 µg/ml) alone, together with SAHA (5 µM) (A) MS-275 (2 µM) (B) or SB (3 mM) (C) and after pretreatment for 1 h with the NFkB inhibitor Helenalin (20 µM). Represented are the results of four independent experiments carried out in biological triplicates. Shown are relative copy numbers of hBD2 per 10 ng total RNA normalized to βactin expression. *p < 0.05 evaluated by Mann-Whitney u test. (D) Diagram of the used hBD2 promotor constructs (bp −2338 to −1 linked to the luciferase gene). Two NF-κB binding sites and one AP1 binding site are marked relative to the hBD-2 transcription start. Constructs with mutated binding sites were used as indicated. (E) Transfection of CaCo-2/TC7 cells took place with either the wild-type (hBD2-2338-luc) or the mutated hBD2 promotor constructs together with a Renilla luciferase plasmid as internal standard. 24 hrs post transfection, cells were treated with EcN (3 × 108 CFU/ml) for 18 hrs, with SAHA (5 µM) for 20 hrs or a simultaneous combination of both (18 and 20 hrs, respectively). Promotor activation was measured subsequently and is displayed as luciferase activity normalized to Renilla activity. *p < 0.05 evaluated by Wilcoxon signed rank test.