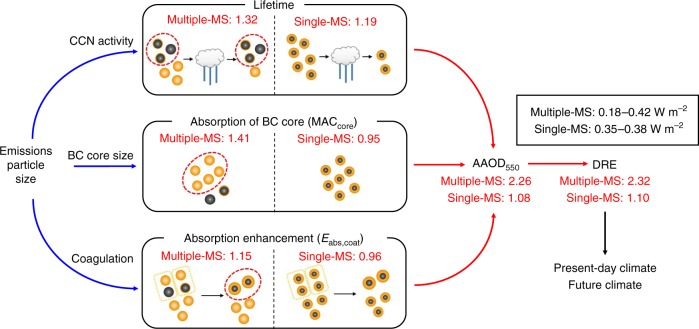
Fig. 4.
Causes of high sensitivity of black carbon direct radiative effect by resolving mixing state. The flowchart shows why the Multiple-mixing-state representation results in high sensitivity of black carbon (BC) direct radiative effect (DRE) due to emission size distributions. Blue and red arrows show negative and positive responses, respectively, in the Multiple-mixing-state representation. Specifically, decreasing particle sizes at emission (e.g., Small-size simulation) increases BC lifetime, BC core absorption, and absorption enhancement, and these enhancements increase absorption aerosol optical depth at 550 nm (AAOD550) and DRE of BC in the Multiple-mixing-state representation. The values shown by red are the ratios between the Small-size and Large-size simulations. The representation of particles in red circles is especially important for accurate calculations of the lifetime (pure BC and thinly-coated BC particles), BC core absorption (BC-free particles), and absorption enhancement (thickly-coated BC particles) effects, which are the causes of different BC DRE sensitivity between the Multiple-mixing-state and Single-mixing-state representations