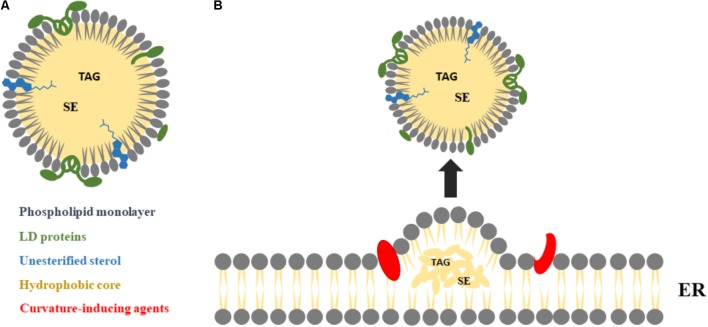
FIGURE 1.
Major LDs morphological features and biogenesis. (A) LDs are composed by a neutral core of triacylglycerols (TAGs) and sterol esters (SEs), surrounded by a monolayer of phospholipids and unesterified sterol, with several proteins at the surface and/or partially integrated within their structure, mainly from the PAT family: perilipin 1 (PLIN1), perilipin 2 (PLIN2), and perilipin 3 (PLIN3). (B) LDs are derived from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), as a result of TAG and SE molecules accumulation between the two leaflets of the ER membrane. The nascent droplets grow into mature LDs, with the help of curvature-inducing agents, and may remain attached to the ER (not shown) or detach from the ER into the cytosol.