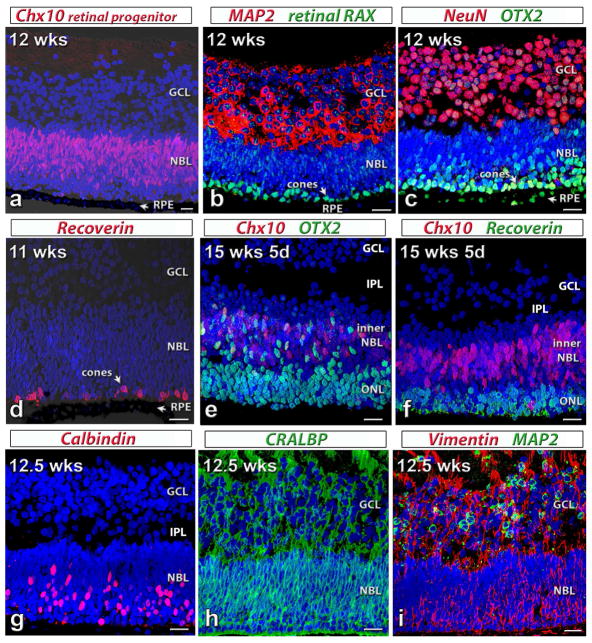
Figure 1. Characterization of human fetal (HF) retina by immunohistochemistry.
Nuclei are stained by DAPI (blue).
(a)–(c): 12 weeks postconception. The retina contains a thick ganglion cell layer (GCL) and a neuroblastic layer (NBL). Arrow: retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). (a) Ch×10 (red, retinal progenitor cell marker) in neuroblastic layer (NBL).
(b) Cytoplasm of most cells in GCL: strongly label for MAP2 (microtubule-associated protein 2, red). Retinal RAX (retinal Homeobox protein, green): faint immunoreactivity in all nuclei; strong stain of nuclei of developing cones. (c) Intense NeuN (neuronal nuclei, red) stain of most ganglion cells. Strong OTX2 (Orthodenticle Homeobox 2, green) staining in RPE and developing photoreceptors.
(d) 11 weeks postconception. Recoverin (red): scattered differentiating cone photoreceptors in NBL close to RPE.
(e,f) 15 weeks 5 d postconception. The outer nuclear layer (ONL) has separated from the inner NBL. Retina has developed an inner plexiform layer (IPL). (e) Strong OTX2 (green) staining in developing photoreceptors and cells in inner NBL, some co-expressing Ch×10 (red). (f) Recoverin (green) staining of several layers of developing photoreceptors. Ch×10 (red) staining in inner NBL.
(g–i) 12.5 weeks postconception. (g) Calbindin (red) staining of developing horizontal cells and cones in outer NBL. (h) CRALBP (cellular retinaldehyde protein, green) immunoreactivity of developing Müller cells. (i) Strong Vimentin (red) staining throughout. MAP2 (green) staining in GCL.
Scale bars: 20 micron.