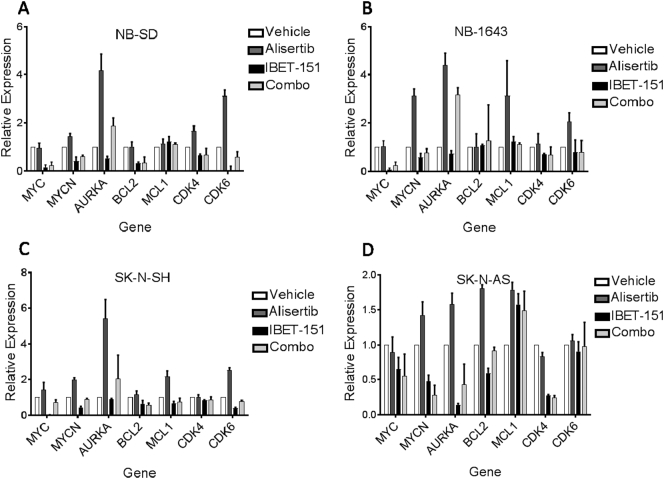
Figure 2.
AURKA inhibition with alisertib induces increased RNA expression of oncogenes, which is mitigated by BRD4 inhibition with I-BET151. Cells were treated with 1 μM I-BET151, 1 μM alisertib, both drugs, or vehicle control for 24 hours, after which RNA was extracted from each cell line and used for RT-qPCR. Treatment with alisertib alone (dark gray bars) induced overexpression of most oncogenic targets tested in NB-SD (A), NB1643 (B) and SK-N-SH (C) cells, with less of an effect on SK-N-AS (D) cells except for AURKA. Co-treatment of the cells with I-BET151 reduced or entirely abrogated this overexpression for most target genes in all four cell lines. Relative expression shown using ddCt methods, with each gene's expression normalized first to housekeeping genes in each sample then against each gene's expression in the vehicle control. Three independent experiments performed, with mean and standard error plotted; one-way ANOVA based on treatment for NB-SD among the four treatment groups P = 0316, for NB1643 P = .0169, for SK-N-SH P = .0482, and for SK-N-AS P = .0079.