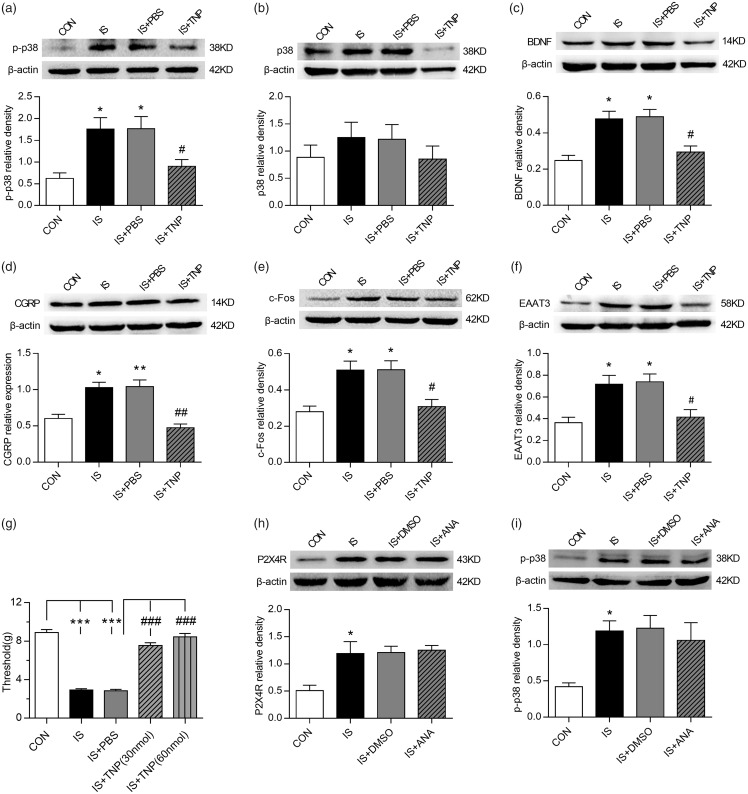
Figure 3.
P2X4R and related signaling pathways were involved in EAAT3 regulation and trigeminal allodynia following repeated dural stimulation. (a) WB for p-p38 expression in the TNC (upper panel) revealed that p-p38 protein level was increased in the IS group compared with the CON group. TNP-ATP (30 nmol) treatment repressed its expression as compared to the group of IS+PBS. Quantification (lower panel) of WB experiments was normalized to actin control. (b) WB for p38 expression in the TNC (upper panel) revealed no evident difference among the four groups. Quantification (lower panel) of WB experiments was normalized to actin control. (c) to (f): WB for BDNF (c), CGRP (d), c-Fos (e), EAAT3 (f) expression in the TNC (upper panel) revealed that BDNF, CGRP, c-Fos, and EAAT3 were all upregulated following repeated dural stimulation as compared to control. TNP-ATP (30 nmol) treatment decreased their protein levels compared with the group of IS+PBS. There were no obvious difference between the group of IS and IS +PBS. Quantification (lower panel) of all WB experiments was normalized to actin control. (g) TNP-ATP treatment significantly increased the basal periorbital pressure thresholds compared with IS+PBS group. The IS+TNP-ATP (30 nmol) and IS+TNP-ATP (60 nmol) groups showed no obvious difference in anti-nociceptive effect. (h) and (i): WB for P2X4R (h), p-p38 (i) expression in the TNC (upper panel) revealed that ANA-12 (100 nmol) treatment did not reverse IS-induced P2X4R and p-p38 upregulation. Quantification (lower panel) of WB experiments was normalized to actin control. Data represent the mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA, followed by a Tukey test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. CON, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. IS+PBS (n = 6 per group).
WB: western blot; IS: inflammatory soup; CON: control; PBS: phosphate-buffered saline; BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; CGRP: calcitonin gene-related peptide; EAAT3: excitatory amino acid transporter 3.