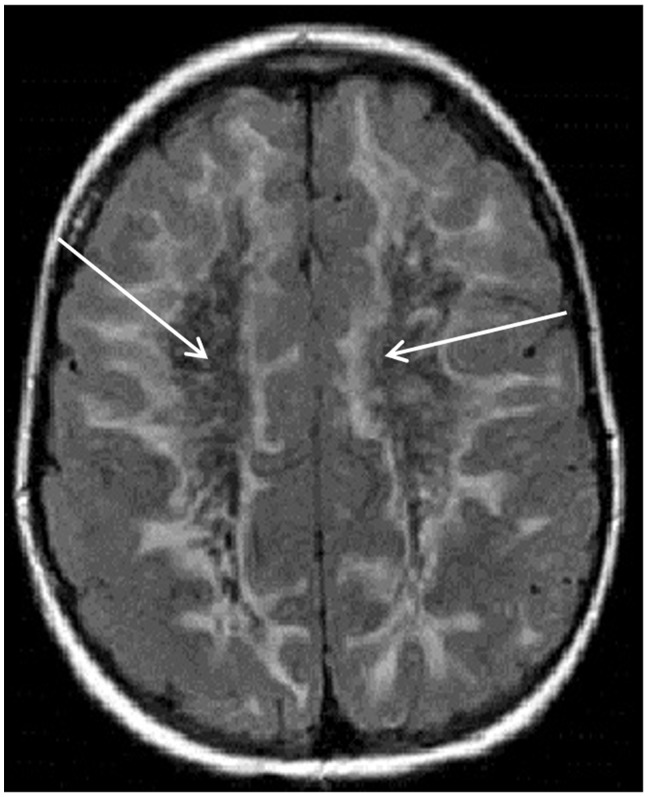
Figure 1.
Axial fluid-attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance imaging scan of the brain showing extensive white matter hyperintensity extending to the subcortical U-fibers. The central white matter suppresses with signal similar to cerebrospinal fluid (see white arrows) in this patient with vanishing white matter disease.