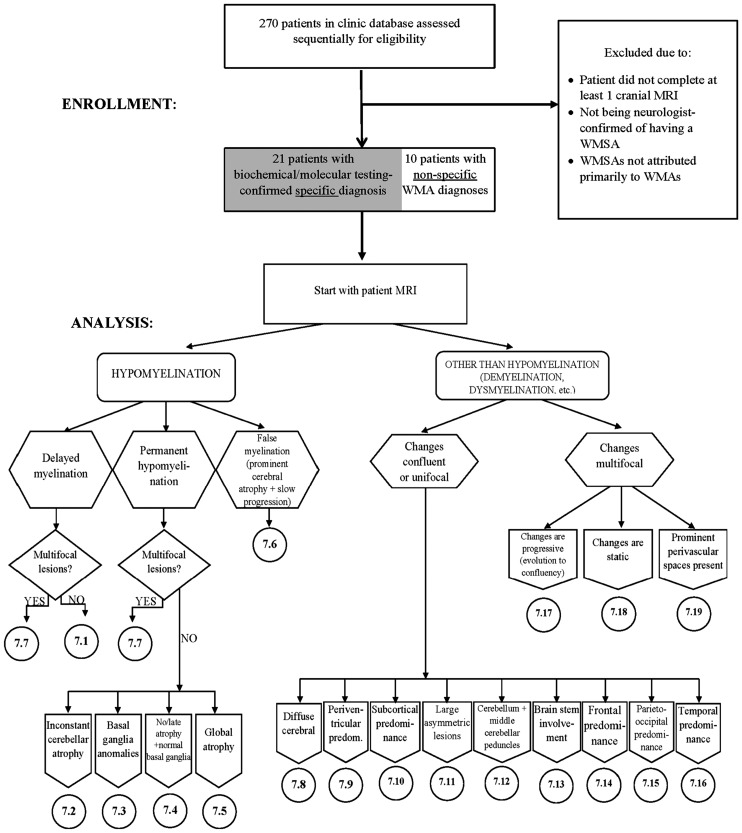
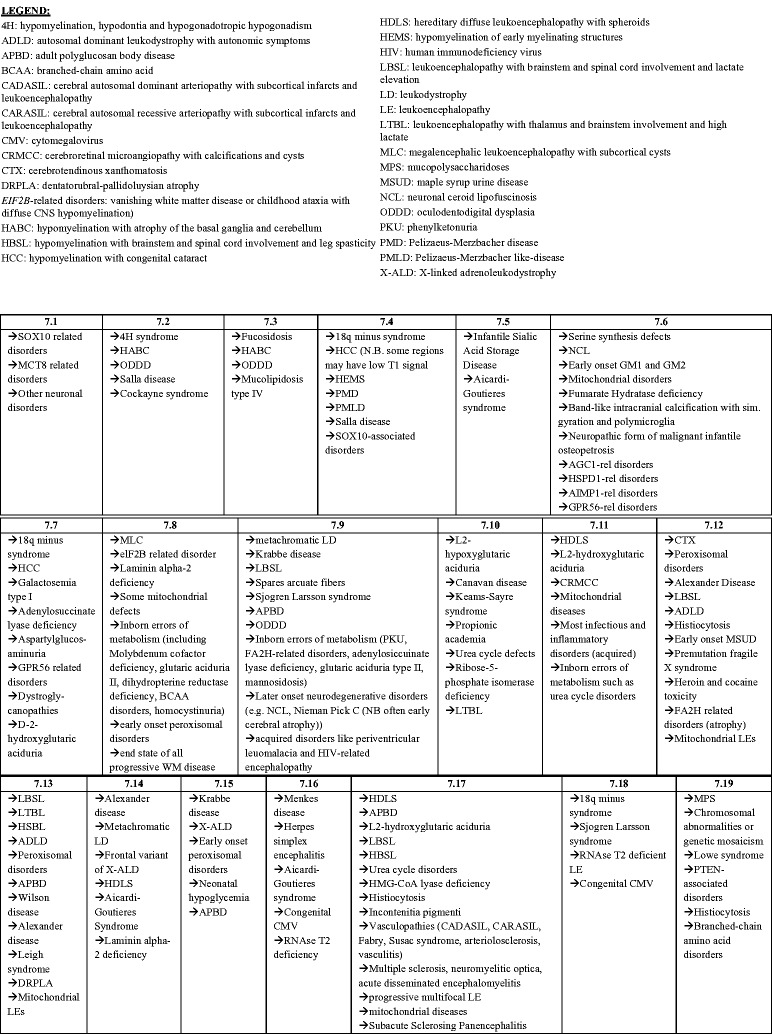
Figure 4.
The magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) algorithm used for the analysis of white matter signal abnormalities (WMSAs) on patient cranial scans. The radiologist began by identifying whether the signal abnormality was indicative of hypomyelination or another type of myelin pathology (dysmyelination, demyelination, etc.). Within the type of myelination present, the radiologist proceeded through the algorithm down the paths that were most applicable to the WMSAs on the scans. Once at a concluding category, denoted by 7.##, the radiologist consulted the patient clinical data to determine differential diagnoses contained in that numerical category. Up to three possible differential diagnoses were allowed for each patient. For each differential diagnosis, a confidence value of 1–10 was assigned. This algorithm, the categorical organization and legend abbreviations are identical to those published by Parikh et al., but the presentation is different.10