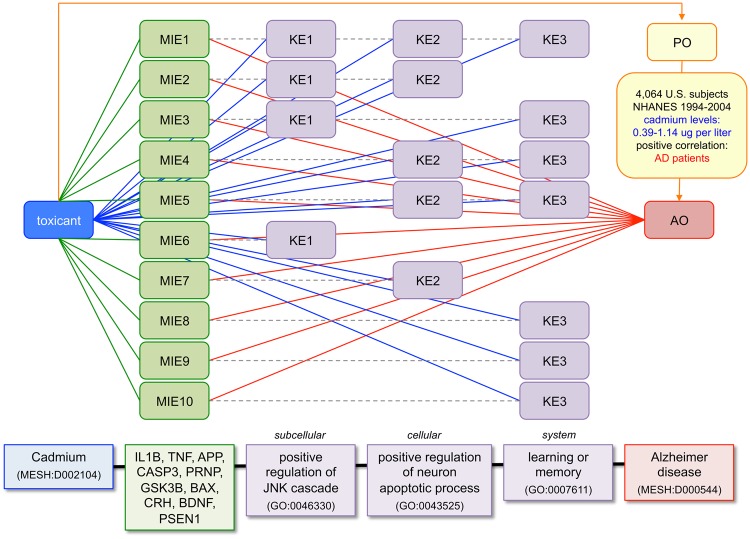
Figure 7.
Integrating CTD content to generate predictive AOPs. Curated content from CTD toxicogenomic core is used to identify 10 molecular initiating events (MIE1-10) relating the toxicant cadmium to 10 genes that are also directly associated with the AO of AD from disease core. CTD's chemical-phenotype curation module fills in the intermediate KEs. Here, just 3 of the 58 prioritized phenotypes (KE1-KE3) are depicted that are directly influenced by cadmium in addition to being independently annotated to the same 10 genes by external GO databases (dotted lines). Phenotypes are organized into 3 KE levels (KE1 subcellular, KE2 cellular, and KE3 system) to generate a predicted AOP (bottom) connecting cadmium to AD. Furthermore, the association of cadmium exposure to AD is confirmed at the PO by CTD's exposure module (top arrow), with a U.S. study correlating cadmium blood levels (0.39-1.14 micrograms per liter) with patients.