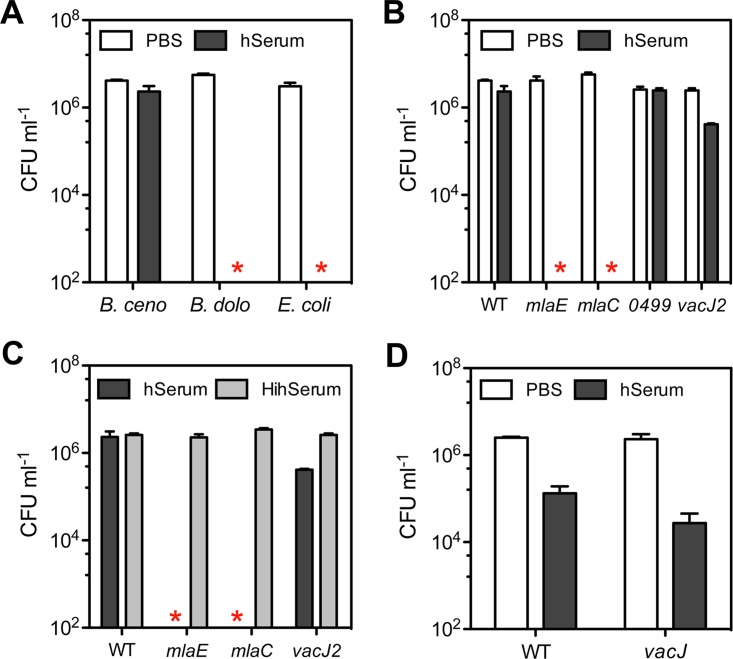
FIG 6.
The role of the Mla pathway in serum resistance. (A) Resistance to 30% human serum (hSerum) over a period of 2 h was evaluated for B. cenocepacia K56-2 (B. ceno), B. dolosa PC543 (B. dolo), and E. coli K-12 strain BW25113 (E. coli). (B) Resistance to 30% hSerum of the mlaC, mlaE, and BCAL0499 insertional mutants and the vacJ2 Tn mutant in comparison to WT B. cenocepacia K56-2. (C) The killing activity of 30% heat-inactivated human serum (HihSerum) was tested with mlaC and mlaE insertional mutants, the vacJ2 Tn mutant, and WT B. cenocepacia K56-2 and compared to that of hSerum. (D) Resistance to 30% hSerum of a vacJ mutant compared to its WT P. aeruginosa PA14 parent strain. Stars represent the absence of recovered CFU or below the detection limits (∼200 CFU). All data represent means ± SD from three replicates.