Figure 1. Selection scheme for AAV variants.
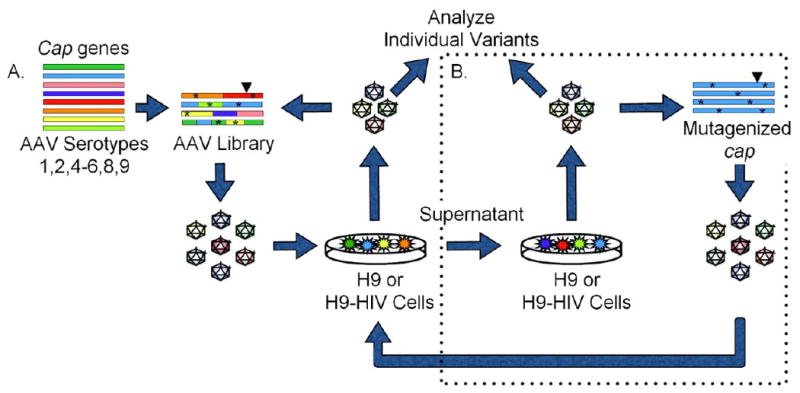
(A) A library of AAV mutants was packaged and used to infect either H9 or HIV-infected H9 cells. Wild-type adenovirus was added as a helper virus to induce replication of AAV that had infected the cells, and the resulting AAV clones were recovered by PCR amplification and cloning their cap genes, which were then re-packaged for two subsequent infections. (B) After three selections, isolated cap genes were subjected to error-prone mutagenesis and three additional rounds of selection were performed including a negative selection step, whereby virus was pre-incubated with the opposite cell line before infecting the cell line of interest. Asterisks (*) represent point mutations; Triangles (▼) represent peptide insertion.
