Table 4.
EmrE inhibitor peptides designed on the basis of the H4 -helix
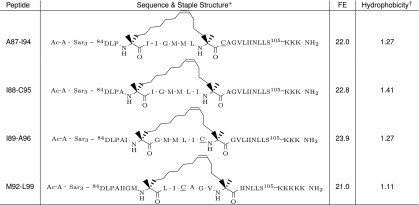 |
The staple structures are adapted from Guo et al. (38). The free energy of separation from EmrE (FE) is expressed in kcal/mol and has an SE of ∼1 kcal/mol.
*Peptide sequences are shown with attached sarcosine (Sar) and lysine (K) tags. Ac and NH2 denote acetylation and amidation of N and C termini, respectively. Alanine-sarcosine and lysine tags were present in experiments only; acetylated and amidated termini were used both in experiment and in simulation. In the experiments, the wild-type C95 in peptides A87–I94, I89–A96, and M92–L99 was replaced with a serine (underlined symbol) to prevent disulfide cross-linking.
†Core peptide hydrophobicity was calculated by the Liu–Deber hydrophobicity scale (39) for each residue and averaged over the sequence (tags and staples were excluded).
