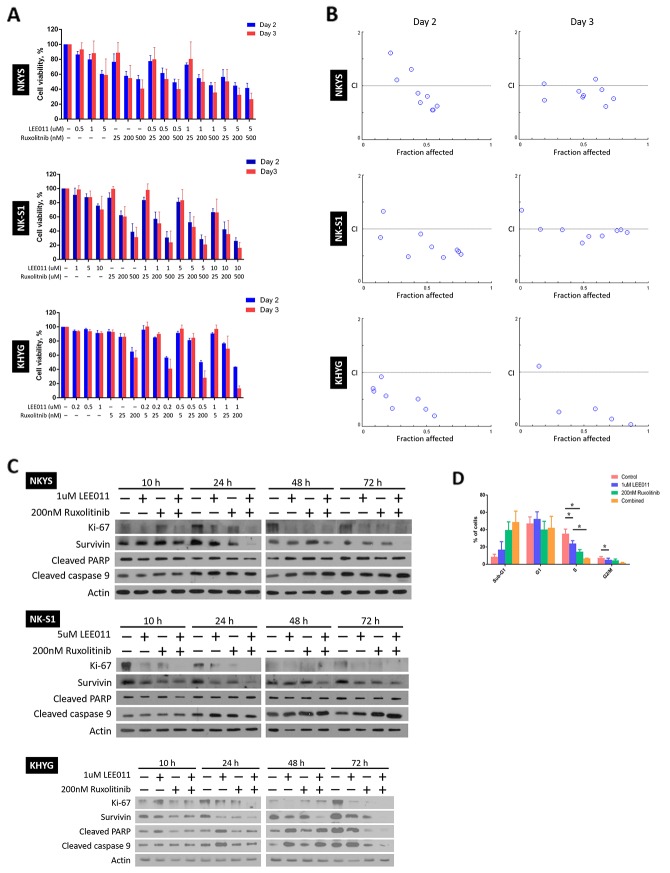
Figure 3. LEE011 and ruxolitinib displayed synergistic relationship on achieving growth inhibition in NKTCL cell lines.
(A) Cell viability assay showed enhanced growth inhibition with dual LEE011 and ruxolitinib treatment. The cells were subjected to single or combined LEE011 treatment as indicated and cell viabilities were assessed on Day 2 and 3. In each experiment, values from triplicate wells were averaged and treatment wells were normalised against control wells. Data is expressed as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. (B) Fa-CI plots for the cells on the days cell viabilities were assessed revealed a synergistic growth inhibition effect with dual treatment of LEE011 and ruxolitinib. In the Fa-CI plots, the dashed line where CI = 1 indicates an additive reaction between the two drugs. Points that fall above (CI>1) and below (CI<1) the dashed line denote antagonism and synergism respectively. (C) Western blot analysis of proliferative and apoptotic markers following LEE011 and ruxolitinib combined treatment. Cells were singly and combine treated to LEE011 and ruxolitinib at concentrations as indicated. Protein lysates from 10 and 24 h were ran on the same SDS-PAGE gel, while that of 48 and 72 h were ran on a separate gel. In general, a decrease in proliferative markers and increase in apoptotic markers in combine treatment as compared to single treatment were noted across different time points. (D) Evaluation of combination treatment using flow cytometric analysis of cell cycle populations. KHYG cells were treated with LEE011 and ruxolitinib at concentrations as indicated. Significant decrease in S phase populations was noted between single LEE011 and combine treatment (n = 3, * p<0.05, one-way ANOVA test).