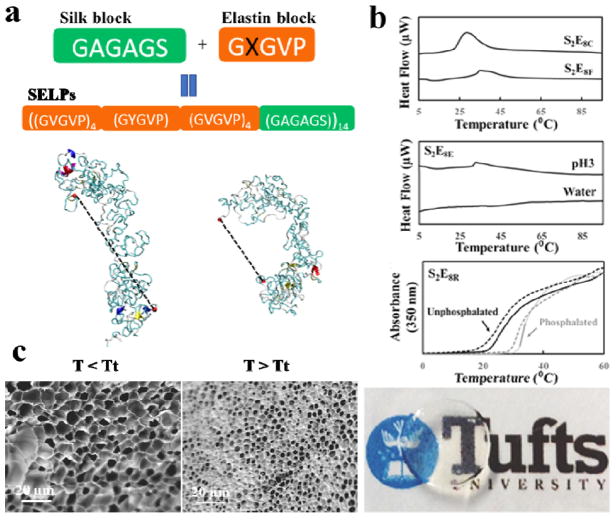
Figure 15. Silk-elastin-like protein dynamic hydrogels.
(a) SELP sequences and representative structures from simulation, at (i) 7 and (ii) 57°C. Dotted lines represent end-to-end molecular distance. (b) SELPs respond to temperature, a physical stimulus, exemplified by SELP with cysteine and phenylalanine mutation in the elastin domains, S2E8C and S2E8F; SELPs respond to pH, a chemical stimulus, exemplified by SELP with glutamic acid mutation in the elastin domains, S2E8E; and SELPs respond to phosphorylation, a biological stimulus, exemplified by with arginine mutation in elastin domains, S2E8R. (c) SEM images showing the micromorphology changes of S2E8R hydrogel samples in swollen states at 4°C (<LCST) and in contracted states at 37°C (>LCST) in deionized water. Adapted with permission from refs 18 and 49. Copyright 2016 WILEY-VCH and 2017 American Chemical Society.