Figure 3. Lithography of silk-based biomaterials.
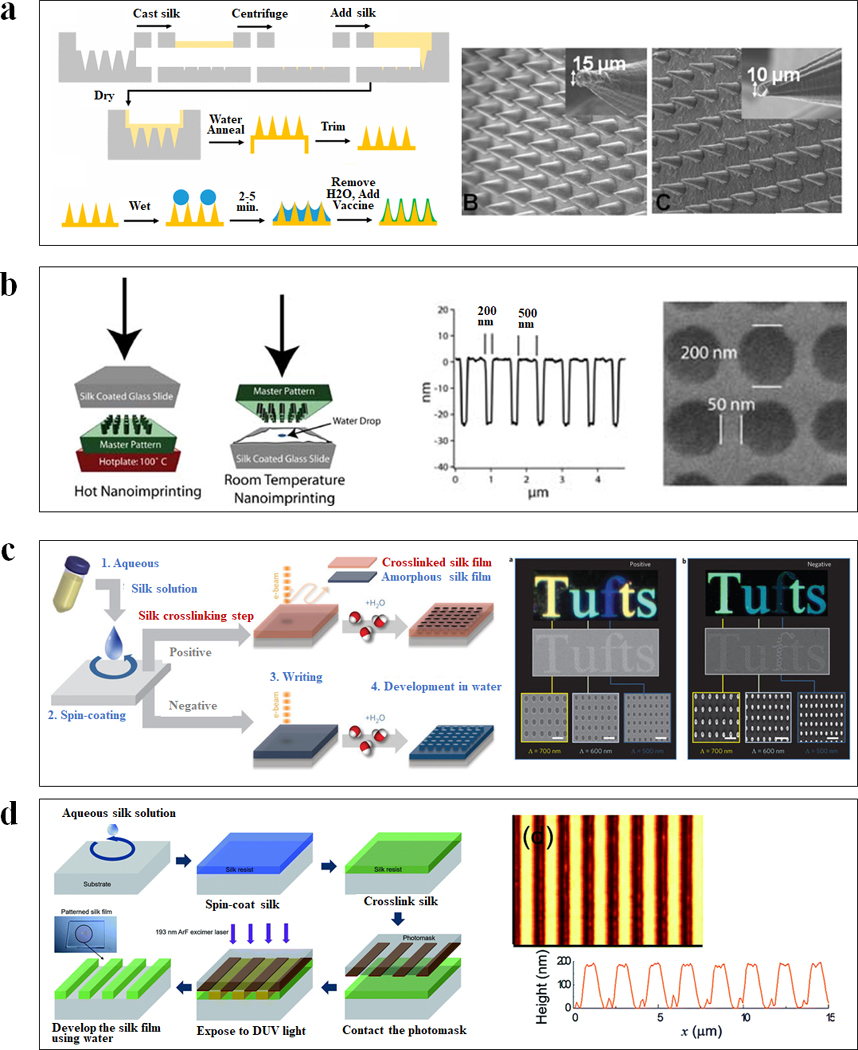
(a) Schematic of soft lithography for vaccine-coated silk fibroin microneedles. SEM images of cone shaped microneedles prepared from an aqueous silk solution with different shapes and geometries. (b) Schematic diagrams of two nanoimprinting processes: hot embossing and room-temperature embossing. SEM image of a silk film imprinted with a periodic array of 200 nm diameter 30 nm height chromium nanoparticles separated by 250 nm. (c) Schematic of all-water-based electron-beam patterning on a silk film. Dark-field and electron microscopy images of silk nanostructures generated on positive and negative resist. (d) Schematic diagrams showing the ArF excimer laser photolithography process to form high-resolution silk fibroin micropatterns. Atomic force microscopy image of the patterned silk suggested the feature was around 190 nm in height and 1 μm in line width. Adapted with permission from refs 21, 23, 26, 27 and 28. Copyright 2010 WILEY-VCH, 2013 WILEY-VCH, 2014 Springer Nature, 2016 The Royal Society of Chemistry and 2017 American Chemical Society.
