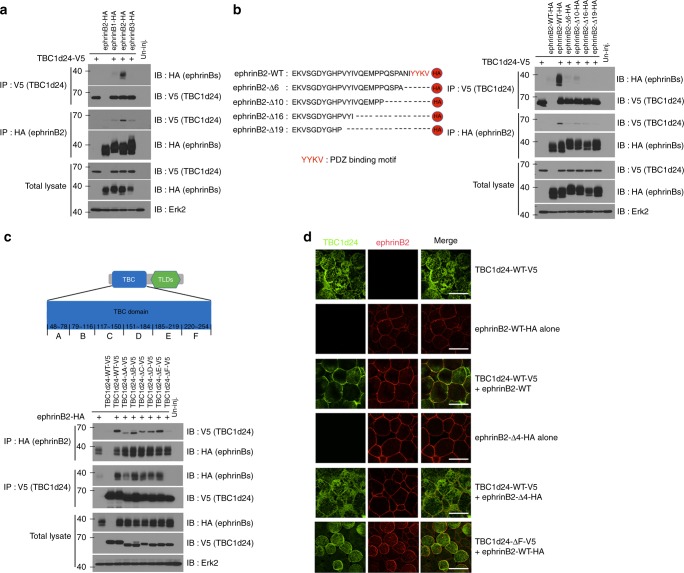
Fig. 1.
TBC1d24 interacts with ephrinB2. a Co-immunoprecipitation assay (Co-IP) using gastrula embryos (stage 10) injected with TBC1d24-V5 RNA (500 pg) and ephrinB1-HA (300 pg), ephrinB2-HA (500 pg) or ephrinB3-HA RNAs (300 pg) show that TBC1d24 interacts with ephrinB2. b Illustration of serial deletion mutants from the C-terminus of ephrinB2. Co-IP using gastrula embryos injected with RNA encoding TBC1d24-V5 and HA-tagged ephrinB2 serial deletion mutants shows that the PDZ binding motif (Δ6) of ephrinB2 is required for TBC1d24 interaction. c Illustration of the amino acid stretches representing regions deleted within the TBC domain. Co-IP using gastrulas injected with RNA for ephrinB2-HA and TBC1d24-V5 serial deletion mutants shows that the F region within the TBC domain of TBC1d24 is critical for an ephrinB2 interaction. d Immunofluorescence microscopic analysis (IF) shows that membrane localisation of V5-tagged TBC1d24 was induced by wild-type ephrinB2 but not ephrinB2-Δ4. Animal caps were dissected at stage 10 and then immunostained for ephrinB2 (red) and TBC1d24 (green). Bar, 50 μm