Fig. 3.
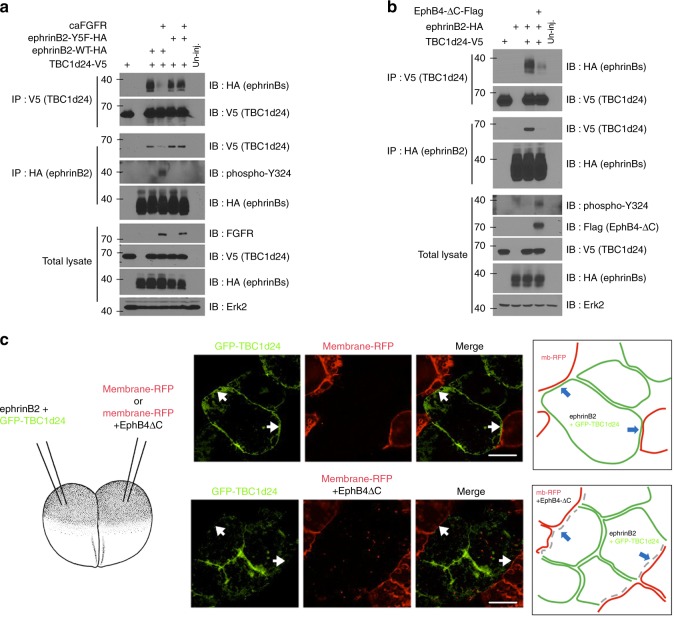
The interaction between ephrinB2 and TBC1d24 is disrupted by tyrosine phosphorylation. a Co-IP using gastrula embryos injected with RNA for TBC1d24-V5 and wild-type ephrinB2-HA or the ephrinB2 tyrosine mutant (Y5F) along with a constitutively active mutant of FGFR1 (caFGFR; 250 pg) shows that ephrinB2 phosphorylation suppresses the interaction between TBC1d24 and ephrinB2. b Co-IP using gastrula embryos injected with RNA encoding TBC1d24 and ephrinB2 wild type along with EphB4-ΔC (having a truncated cytoplasmic domain) (1 ng) shows that the interaction between ephrinB2 and the ectodomain of its cognate receptor EphB4 inhibits ephrinB2–TBC1d24 binding. c IF of ectoderm tissue excised from the embryos injected with the indicated RNAs shows that membrane localisation of GFP-TBC1d24 (green) in ephrinB2-expressing cells is dramatically reduced at the site of cell–cell contact with cells expressing both EphB4-ΔC and membrane-RFP (red). However, membrane localisation of GFP-TBC1d24 is unaffected by contact with only membrane-RFP-expressing cells. The white arrows indicate cell–cell contact regions. The cartoon depicts areas in the merged image. Bar, 20 μm