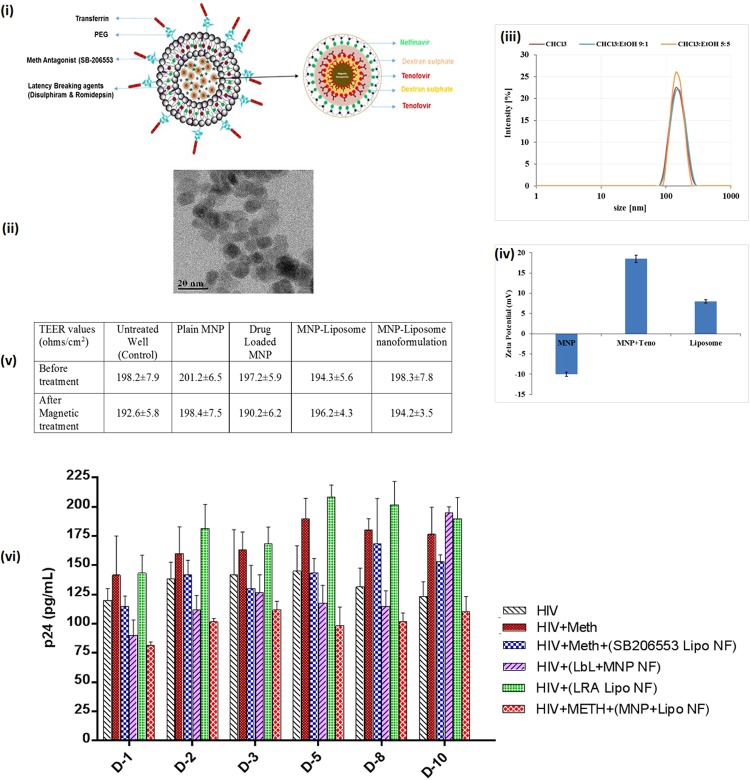
Figure 3.
Nanoformulation (NF) design, characterizations and efficacy evaluation: (i) Schematic representation of nanoformulation design; (ii) Transmission electron microscopy of MNPs, average size range: 10 ± 3 nm (iii) hydrodynamic size of magneto-liposome in different solvent condition; (iv) Zeta potential analysis of blank MNP, 1BL coated drug loaded MNP and drug loaded magneto-liposome in PBS; (v) Transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER) values of the in-vitro BBB model before and after treatment of NF in the presence and absence of external magnetic force; (vi) NF efficacy in HIV-1 infected HA in presence of Meth: HA (1 × 105 cells) were grown in 6 well culture plates and cells were infected with 20 ng of HIV-1 clade B for overnight. Unbound virus was washed with PBS and cell were infected for 14 days so that cell goes into Latent phage. On the 15 day of infection, optimized Meth (25 µM) was added to cells and treated every day for next 10 days (total 25 days of HIV infection). Drug-loaded NF (100 µg/ml) was added only once (on the16 day) to the respective wells and effect of NF on HIV infection ± Meth levels were measured by using the p24 ELISA. Results were analyzed with respect to HIV-1 v/s HIV-1+ Meth v/s NF treatment (*p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001; ****p ≤ 0.0001; NS-Not Significant); Standard errors are shown for the mean of triplicate samples. TEM-Magnification 200 K, Scale bar –100 nm.