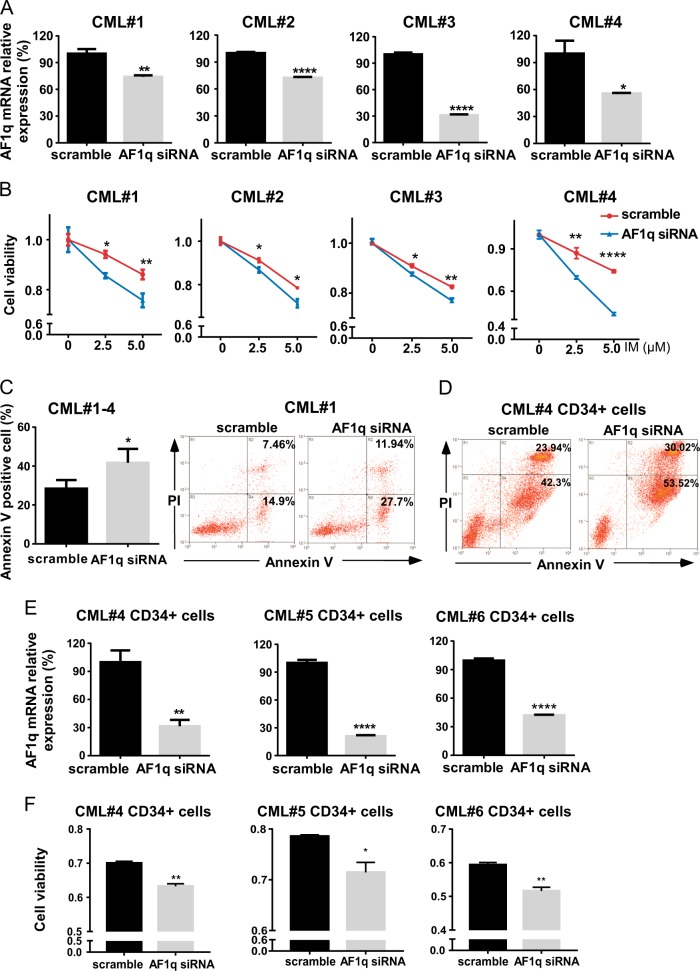
Fig. 2. AF1q inhibition enhanced IM sensitivity and promoted IM-induced apoptosis in CML primary and CD34+ cells.
a Primary BMMCs from newly diagnosed CP CML patients (n = 4) were transduced with AF1q siRNA or scrambled control sequences. AF1q expression in primary CML cells was estimated by qRT-PCR with β-actin as an internal control. b Cell viabilities of primary CML cells transduced with AF1q siRNA or scrambled control were assessed by CCK-8 after IM treatment (48 h, 2.5 or 5 μM). c Primary CML cells transduced with AF1q siRNA or scrambled control were cultured with IM (5 μM, 48 h) and apoptosis was measured by flow cytometry with dual staining of Annexin V and PI. Representative dot plots and graphs are shown. d CD34+ CML cells from CP CML patients transduced with AF1q siRNA or scrambled control were treated with IM (10 μM, 48 h) and apoptosis was measured by flow cytometry with dual staining of Annexin V and PI. Representative dot plots of apoptosis are shown. e CD34+ cells isolated from newly diagnosed CP CML patients (n = 3) were transduced with AF1q siRNA or scrambled control sequences and AF1q expression was estimated by qRT-PCR and normalized to β-actin. f Cell viabilities of CD34+ CML cells transduced with AF1q siRNA or scrambled control were assessed by CCK-8 after IM treatment (48 h, CML#4 5 μM, CML#5 and #6 10 μM). Mean ± SEM. Student t test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001