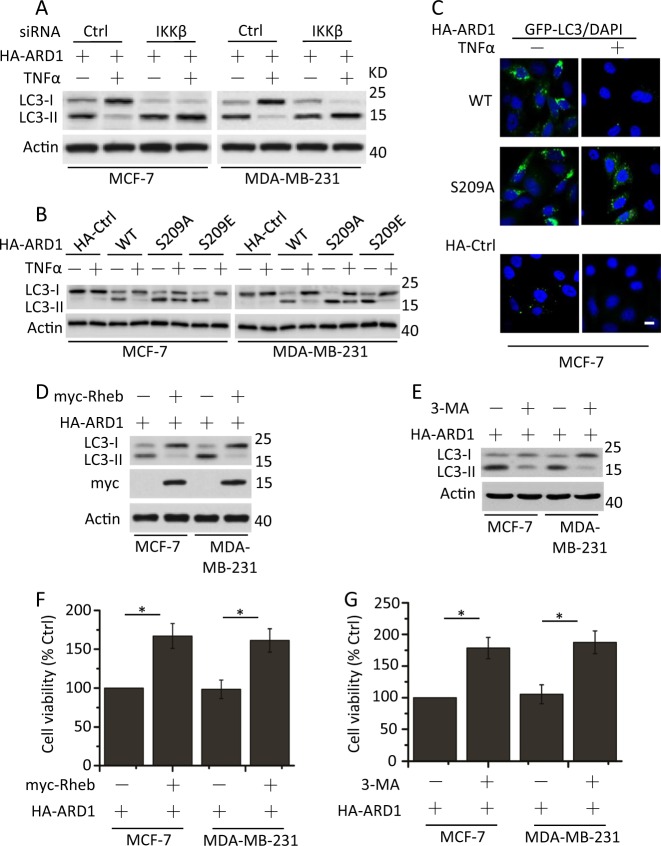
Fig. 3. ARD1 restrains mTOR activity to promote autophagy through regulation of IKKβ.
a MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells were cotransfected with HA-ARD1, Ctrl siRNA, or IKKβ siRNA for 48 h, serum-starved overnight, and then treated with TNFα for 1 h. Cell lysates were collected for detection of LC3-I and LC3-II expression. β-Actin was used as a protein loading control. b Cells were transfected with HA-Ctrl, HA-ARD1 WT, or HA-ARD1 mutants, serum-starved overnight, and then treated with TNFα for 1 h. Treated cells were determined as described in a. c MCF-7 cells were cotransfected with GFP-LC3 and HA-Ctrl, HA-ARD1 WT, or HA-ARD1 S209A, serum-starved overnight, and then treated with TNFα for 1 h. Treated cells were fixed, and then visualized by fluorescent microscopy. Bars, 10 µM. d MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells were cotransfected with HA-ARD1 and myc-Rheb. Cell lysates were collected for LC3-I and LC3-II expression detection. e Cells were transfected with HA-ARD1 and then treated with the inhibitor of class III PI3 kinases 3-MA (5 mM) for 4 h, lysed and subjected to western blotting with anti-LC3 antibodies to monitor autophagy. f and g Cells were treated as described in d and e, respectively. Cell viability and proliferation were determined. Graphs showing the results of quantitative analyses (n = 3, mean ± S.D. *P < 0.05)