FIGURE 1.
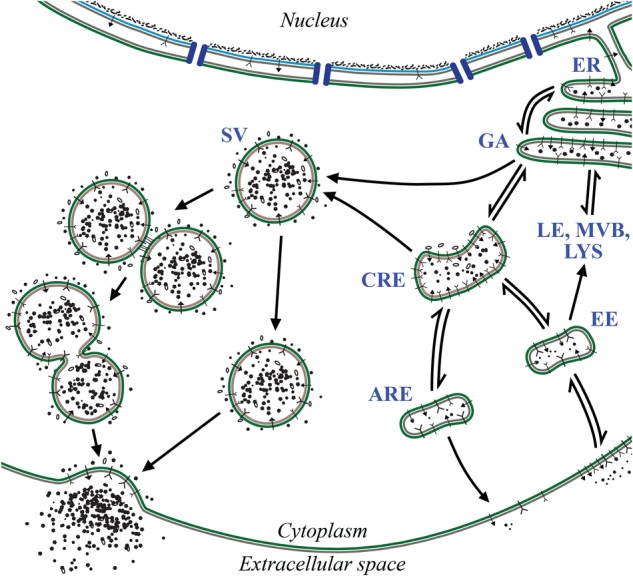
Features of the ERC. The ERC encompasses several vesicle-mediated trafficking events required for diverse cellular activities including maintenance of cellular homeostasis, regulation of growth, and response to danger. Through ERC-related pathways, membrane-bound receptors and other extracellular compounds are endocytosed and routed to the appropriate compartments for signaling, digestion, or exocytosis. Inbound materials enter through early endosome (EE) populations before being routed elsewhere such as common recycling endosomes (CRE), degradative pathways (LE, MVB, LYS), or back to the surface. From CRE compartments, cargo may also be exocytosed through apical recycling endosomes (ARE) or secretory vesicles (SV). During SV exocytosis, vesicles are transported to the plasma membrane and their contents are released by means of individual or compound exocytic events. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus (GA), late endosomes (LE), lysosomes (LYS), multivesicular bodies (MVB).
