Figure 1.
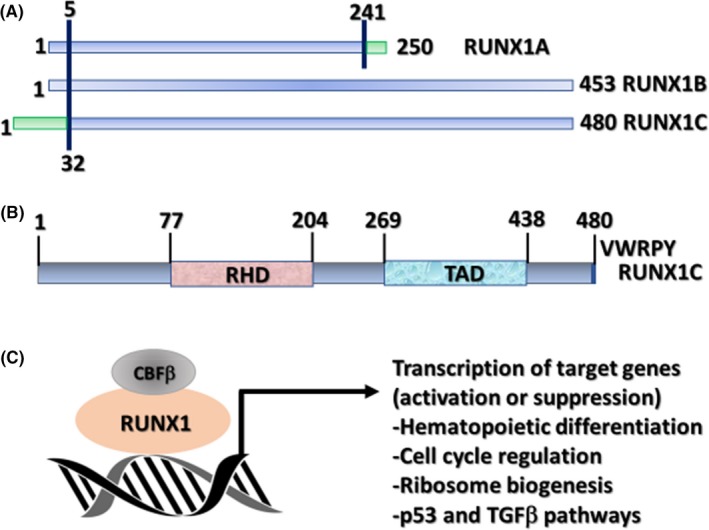
Runt (Runt domain)‐related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) protein and its significant role as a transcription factor. (A) Schemas of the three major isoforms of RUNX1 (RUNX1A, B, and C). (B) Schematic of the protein encoded by the largest isoform (RUNX1C) with major functional domains marked: RUNX homology domain (RHD) and transactivation domain (TAD). Numbers above lines represent amino acid residues. (C) Schematic of RUNX1 heterodimerization with its non‐DNA‐binding partner, core‐binding factor β (CBFβ), and interaction with DNA at promoters of target genes that carry the specific binding site YGYGGTY, where Y is C or T TGFβ, transforming growth factor β. Sood R, Kamikubo Y, Liu P. Role of RUNX1 in hematological malignancies, Blood. 2017;129:2070–20822, ©The American Society of Hematology
This image is not covered by the terms of the Creative Commons license of this publication. For permission to reuse, please contact the rights holder
