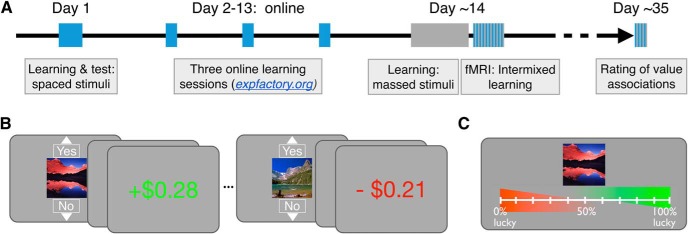
Figure 1.
A, Experimental timeline. Learning for the spaced-trained stimuli is indicated in blue and learning for the massed-trained stimuli is indicated in gray. The initial learning session for spaced-trained stimuli was completed on day 1. Learning for spaced stimuli was then completed in multiple short (massed) sessions, whereas learning for massed stimuli was completed in a single session ∼14 d later. Aside from the separation of spaced learning into multiple condensed sessions, inter-trial timing was matched across conditions. A forced-choice test was also collected after initial learning and the completion of learning. A long-term follow-up measure of reward value using ratings was collected after ∼3 weeks. B, Reward learning task. Participants learned to select “Yes” for reward-associated stimuli and “No” for loss-associated stimuli. Choices were presented for 2 s and feedback followed after a 1 s delay. C, Reward association rating test. This rating phase followed the initial in-lab learning sessions and was also administered 3 weeks after the last learning session.