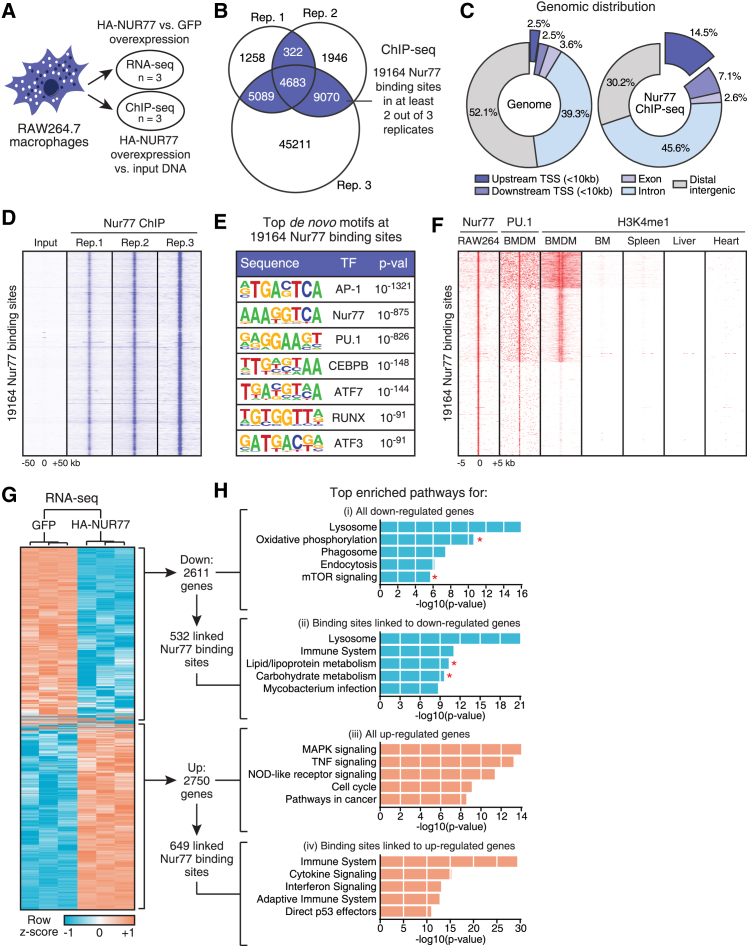
Figure 1.
Genome-wide Binding Site and Transcriptome Profiling Implicate Nur77 in the Regulation of Macrophage Mitochondrial Metabolism
(A) ChIP-seq and RNA-seq experimental setup in RAW264.7 with inducible overexpression of HA-NUR77 or GFP.
(B) Venn diagram of Nur77 binding sites in ChIP-seq dataset. Binding sites present in at least 2 of 3 ChIP replicates were used for further analyses.
(C) Genomic distribution of 19,164 Nur77 binding sites in RAW264.7.
(D) ChIP-seq signal for RAW264.7 input and Nur77 ChIP samples in 100 kb window around 19,164 Nur77 binding sites.
(E) Top enriched de novo transcription factor (TF) motifs within 200 bp of 19,164 Nur77 binding sites.
(F) ChIP-seq signal for Nur77, PU.1, and H3K4me1 in indicated cell types in 5 kb window around 19,164 Nur77 binding sites in RAW264.7.
(G) Hierarchical clustering and Z score heatmap of Nur77-regulated genes as determined by RNA-seq.
(H) Top enriched pathways for genes (i) down- and (iii) upregulated by Nur77 overexpression in RNA-seq dataset or Nur77 binding sites linked to (ii) down- and (iv) upregulated genes in ChIP-seq dataset. Asterisks indicate metabolic pathways.
See also Figure S1.