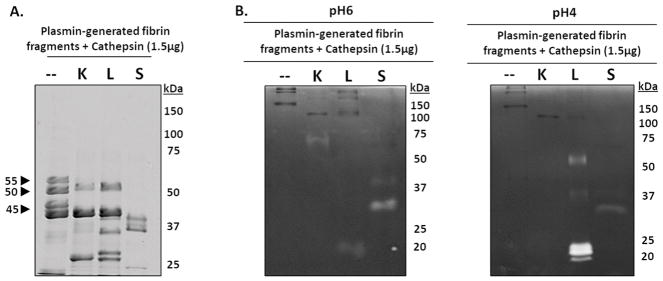
Figure 6. Cathepsins K, L, and S degrade plasmin-generated fibrin fragments.
To identify if cathepsins K, L, or S could successively degrade the released fibrin fragments into smaller molecular weight fibrin fragments, fibrin gels were first incubated with plasmin for 24 hours, then the fibrin fragments released into the supernatant were collected then incubated with catK, L, or S for 24 hours. (A) Compared to the no enzyme control, catK, L, and S successively degraded the fibrin fragments into lower molecular weight fragments. CatS completely degraded the 55kDa, 50kDa, and 45kDa fragments while catK and L only degraded the 55kDa fibrin fragments. (B) From zymography, active catL was at its expected molecular size (20kDa), as well as the higher molecular weights (~50kDa and faintly at 37kDa), corresponding to the results from the dosing and time course fibrin degradation experiments. Active catK is observed at 75kDa. Unbound active catS was observed at 25kDa in the zymograms incubated at pH 6. Active catL appears in the zymograms incubated at pH 4.