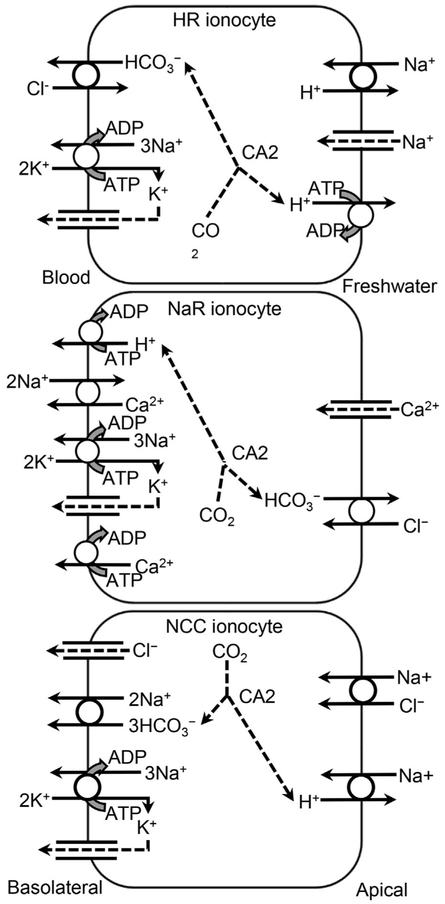
Figure 2.
Current model for transporters on H+-adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase)-rich (HR), Na+/K+-ATPase-rich (NaR), and Na+/Cl−-cotransporter (NCC) ionocytes of fish, such as zebrafish. In the HR ionocyte along the apical membrane are Na+/H+-exchanger (NHE), apical Na+-channel, and vacuolar-type H+-ATPase (VHA), whereas along the basolateral membrane are the anion exchanger (AE), Na+/K+-ATPase (NKA) and K+-channel (KC). In the NaR ionocyte, along the apical membrane are the epithelial Ca2+-channel (ECaC) and anion exchanger, whereas along the basolateral membrane are VHA, Na+/Ca2+-exchanger (NCX), NKA, KC, and plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase (PMCA). In the NCC ionocyte, along the apical membrane are NCC and NHE, whereas along the basolateral membrane are the Cl−-channel, Na+/HCO3−-cotransporter (NBC), NKA, and KC. Dashed arrows indicate diffusion, whereas solid arrows indicate active transport. Arrows that split indicate reactions. Modified from Dymowska et al. [303]. CA2=carbonic anhydrase type 2 enzyme; ATP=adenosine triphosphate; ADP=adenosine diphosphate.