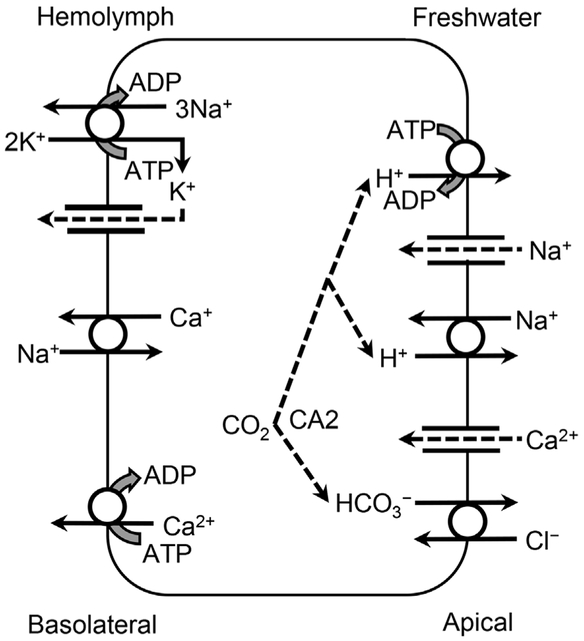
Figure 4.
Generalized model for transporters on epithelial ionocytes of aquatic insects based on transporters identified by the present review. A single cell is shown because no studies have identified different ionocyte types, although research with mosquito larvae suggests that transporters for at least K+ and Ca2+ are not collocated with those for Na+ and Cl− on the anal papillae. Also, the evidence suggests variation among aquatic insect orders. Along the apical membrane are vacuolar-type H+-adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase; VHA), apical Na+-channel, Na+/H+-exchanger (NHE), epithelial Ca2+-channel (ECaC), and anion exchanger (AE). On the basolateral membrane are Na+/K+-ATPase (NKA). K+-channel (KC), Na+/Ca2+-exchanger (NCX), and plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase (PMCA). Dashed arrows indicate diffusion, whereas solid arrows indicate active transport. Arrows that split indicate reactions. CA2=carbonic anhydrase type 2 enzyme; ATP=adenosine triphosphate; ADP=adenosine diphosphate.