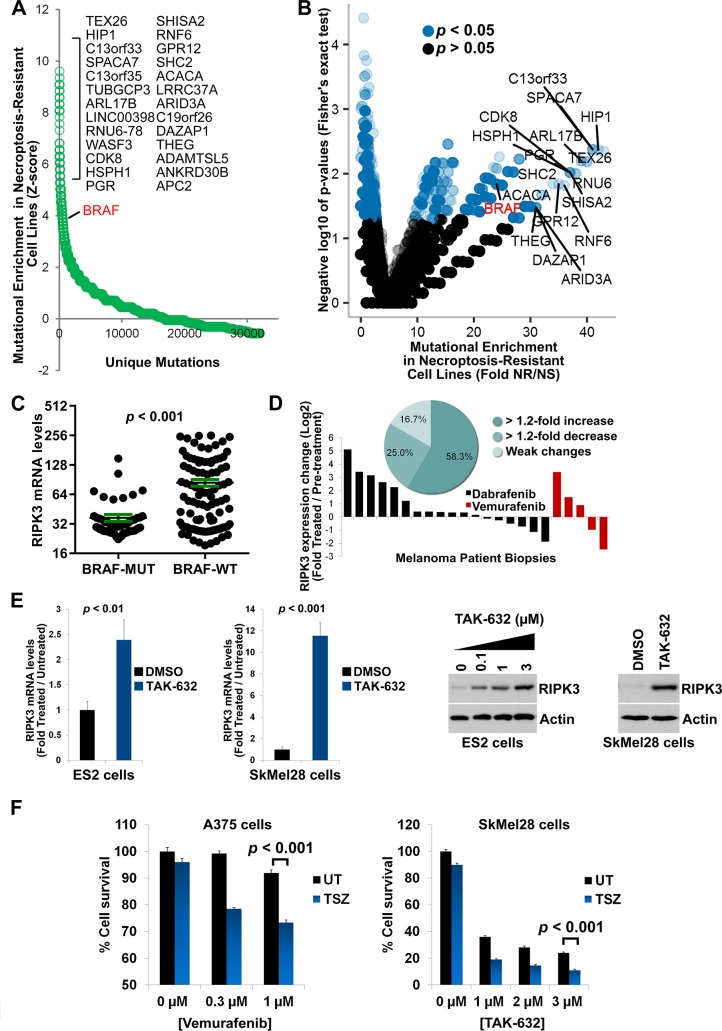
Fig 4. Necroptosis sensitivity screen in 941 cancer cell lines identifies BRAF as a mutational driver of RIPK3 expression loss and gain of necroptosis resistance.
(A) Mutational drivers of necroptosis resistance in cancer. z-score analysis of the fold mutation enrichment in NR versus NS cancer cell lines. BRAF is a top oncogene among genes, the mutation of which is enriched in NR cells. The x-axis depicts the different types of mutations (e.g., amplification, deletion, missense) found per gene. Top hits are indicated. (B) Volcano plot showing the results of the Fisher’s exact test analysis for the mutational enrichment data shown in (A). Top hits are indicated. (C) BRAF-activating mutations (BRAF-MUT, e.g., V600E mutation) predict loss of RIPK3 expression in cancer. GDSC database was employed in the analysis. All BRAF-activating mutations were pooled into one group (BRAF-MUT). (D) Inhibition of BRAF in melanoma patients can rescue loss of RIPK3 expression. RIPK3 mRNA levels are increased in 58.3% of melanoma patient tumor biopsies following treatment with BRAF inhibitors Dabrafenib or Vemurafenib. Inset shows percentages of patients with significant changes in RIPK3 expression (Dataset GEO ID: GSE50509). (E) Inhibition of BRAF in cancer cell lines can rescue loss of RIPK3 expression. qRT-PCR and western blotting analysis of RIPK3 expression in ES2 and SkMel28 cell lines following 4 days of BRAF inhibition by 1 μM of TAK-632. These cell lines were selected because they did not show significant cell death following treatment with this inhibitor. The experiments were repeated two times. Bar graphs show means ± SEM with t test p-values. (F) Inhibition of BRAF in cancer cell lines can rescue loss of necroptosis sensitivity. A375 and SkMel28 cells were treated with indicated concentrations of Vemurafenib or TAK-632 for 4 days. Drugs were washed out and necroptosis was induced by 24-hour treatment with 25 ng/mL TNFα + 0.5 μM SM-164 + 30 μM zVAD.fmk. Cell survival was determined using CellTiterGlo assay. The underlying data can be found in S1 Data. BRAF-MUT, BRAF-activating mutation; BRAF-WT, BRAF wild-type; GDSC, Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer; NR, necroptosis-resistant; NS, necroptosis-sensitive; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time PCR; TSZ, TNFα+SM-164+zVAD.fmk; UT, untreated