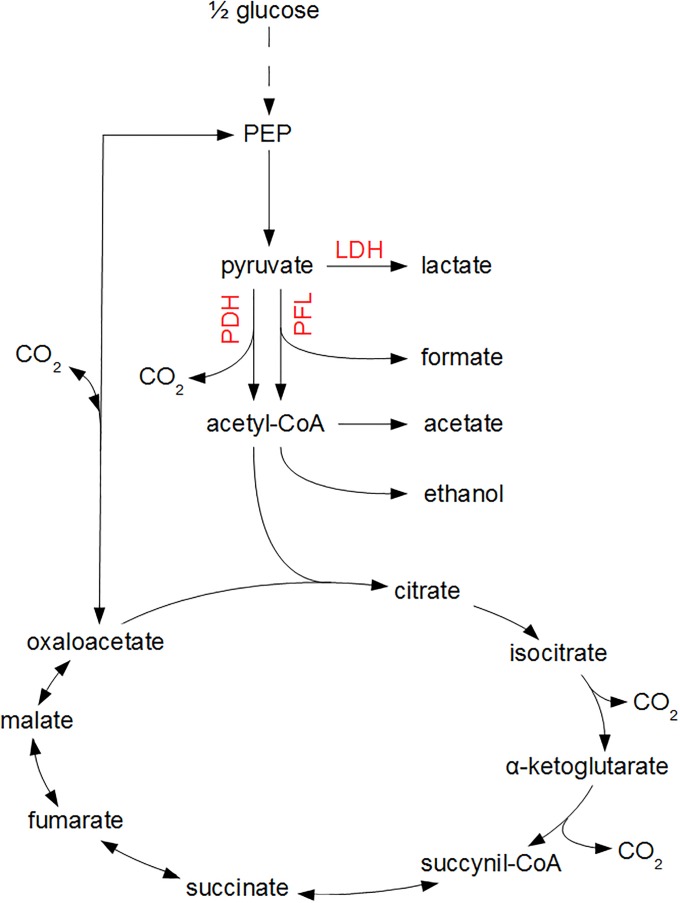
Fig 1. Central metabolic pathways of E. coli.
Glucose is converted to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and pyruvate through the glycolysis pathway, indicated by the dashed line. Subsequently, under oxygen-rich conditions, pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA through the pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) enzyme complex, whereupon acetyl-CoA enters the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) as citrate. Under oxygen-limited conditions, pyruvate reacts to lactic acid through the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) pathway or to formic acid and acetyl-CoA by means of the pyruvate formate lyase (PFL) complex. In the absence of a functional TCA cycle at oxygen limitations, acetyl-CoA is transformed to acetic acid or ethanol.