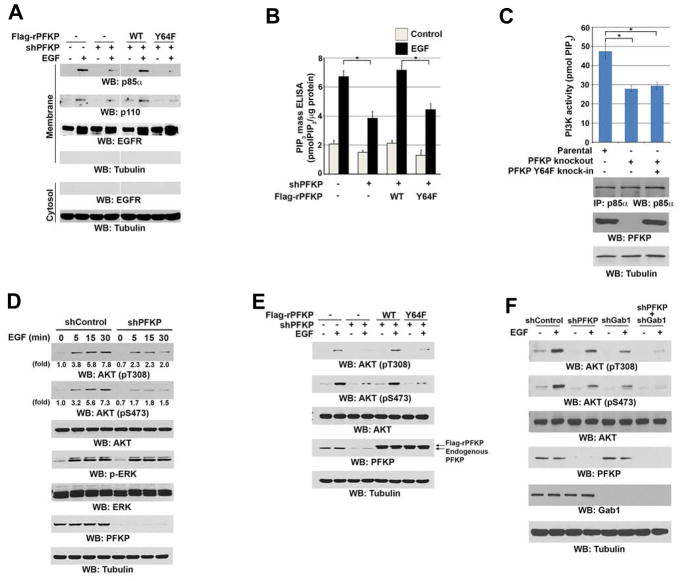
Figure 4. Phosphorylation of PFKP at Y64 Enhances EGF-Induced Activation of PI3K and AKT.
Immunoblotting analyses were performed with the indicated antibodies (A, C–F).
(A, B) Serum-starved U251 cells with or without expressing PFKP shRNA and with or without reconstituted expression of WT Flag-rPFKP or Flag-rPFKP Y64F mutant were treated with or without EGF (100 ng/ml) for 15 min. The membrane and cytosolic fractions of these cells were prepared (A). The intracellular PIP3 levels were determined. Data represent the means ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < 0.01, based on the Student’s t test (B).
(C) PI3K activities of the p85α immunoprecipitates were determined in U87/EGFRvIII cells with or without knockout of PFKP or knock-in of PFKP Y64F mutant. MG132 (10 μM) was added to the cells 6 h before harvesting to eliminate the potential effect of proteasomal degradation of PFKP. Data represent the means ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < 0.001, based on the Student’s t test.
(D) Serum-starved U251 cells with or without expressing PFKP shRNA were treated with EGF (100 ng/ml) for the indicated time periods.
(E) Serum-starved U251 cells with or without expressing PFKP shRNA and with or without reconstituted expression of WT Flag-rPFKP or Flag-rPFKP Y64F mutant were treated with or without EGF (100 ng/ml) for 15 min.
(F) Serum-starved U251 cells with or without expressing PFKP shRNA, Gab1 shRNA, or combined PFKP shRNA and Gab1 shRNA were treated with or without EGF (100 ng/ml) for 15 min.