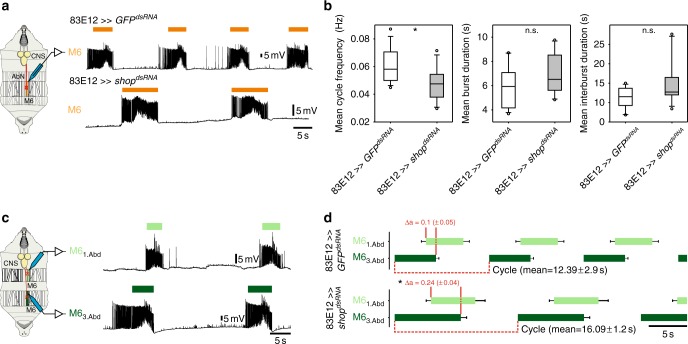
Fig. 3.
Suppression of shopper impairs motor patterns underlying larval locomotion. a Experimental setup for single M6 intracellular muscle recordings of third-instar larvae; representative M6 recordings of (UAS-GFPdsRNA; R83E12-Gal4) (control, n = 15 animals) and (UAS-shopdsRNA; R83E12-Gal4) (n = 11 animals); orange bars indicate M6 bursts. b Box plots show the cycle frequency, burst duration, and inter-burst duration. Knockdown of shopper in the glial cells significantly decreased the cycle frequency compared to the control (UAS-GFPdsRNA; R83E12-Gal4). Box plots comprise the 25–75% coincidence interval, as well as the median. Whiskers comprise the 90% coincidence interval. Outliers are black dots. c Experimental setup for double M6 intracellular muscle recording of the first and third abdominal segment in a third-instar larva. Representative M6 double recording of (UAS-GFPdsRNA; R83E12-Gal4) (Control); M6 motor activity of the third (dark green bars) and the first (light green bars) abdominal segment resembles fictive forward crawling. d Motor pattern of (UAS-GFPdsRNA; R83E12-Gal4) (control, n = 12 animals) and (UAS-shopdsRNA; R83E12-Gal4) (n = 7 animals) while forward crawling. Horizontal box plots represent mean M6 burst activity of first (light green) and third abdominal segment (dark green), whiskers resemble the standard error of M6 burst activity. Dark green boxes represent the time until onset of the next burst in the same segment. This represents the cycle duration. Light green boxes represent the onset and offsets of bursts in the first abdominal segment. Comparing offset of bursts in third abdominal segment with the onset of bursts in the first abdominal segments reveals the phase delay Δa, which is a measure for coordination of the wave of bursts which activates fictive crawling. In addition to the impaired crawling cycle of (UAS-shopdsRNA; R83E12-Gal4), the phase delay (Δa) between offset of motor activity in third abdominal segment and onset of motor activity in the first abdominal segment shows significant difference indicating that coordination of the two abdominal segments is slightly impaired during crawling; *p < 0.05, n.s.: not significant, Mann–Whitney test (b) and two-tailed t-test (d)