Fig. 8.
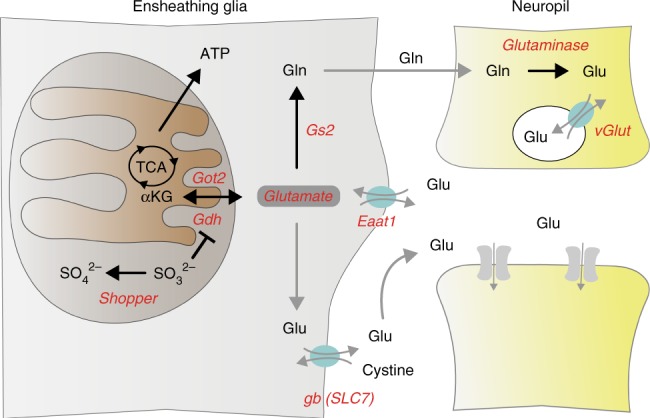
Shopper influences the glutamate metabolism in the nervous system. Schematic view of glutamate homeostasis in glial cells and its contribution to the glutamate–glutamine cycle. Glutamate (Glu) can be generated from α-ketoglutarate (αKG) by glutamate dehydrogenase (Gdh) or from aspartate and α-ketoglutarate (glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase, Got2). Glutamate is then converted to glutamine by glutamine synthetase 2 (Gs2) or is exported by SLC7 type transporters which in Drosophila is Genderblind (gb). In addition, glutamate can be taken up from the extracellular space by the excitatory amino acid transporter 1 (Eaat1). Neurons are able to take up glutamine and glutaminase converts it back to glutamate, which is then transported into synaptic vesicles by the vesicular glutamate transporter (vGlut). Shopper detoxifies sulfite which otherwise inhibits Gdh
