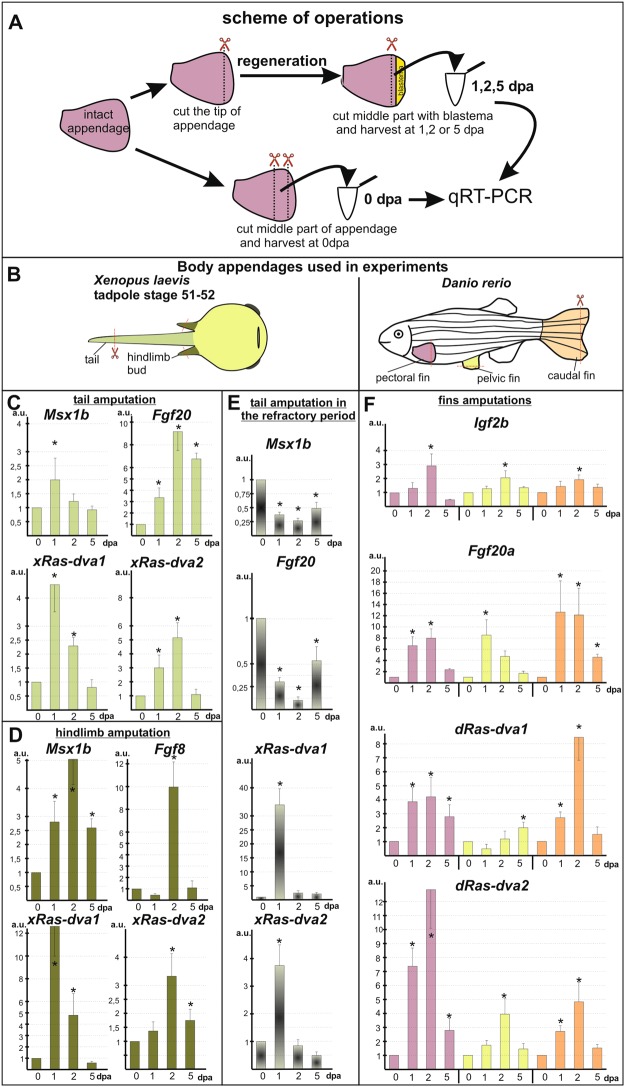
Figure 2.
The qRT-PCR analysis of Ras-dva1, Ras-dva2 and regeneration markers expression in X. laevis tadpoles and D. rerio adult fishes after the body appendages amputation. (A,B) Schemes of experiments. Drawings were done by M.B.T. (C,D) The results of qRT-PCR analysis of xRas-dva1, xRas-dva2 and marker genes (Msx1b, Fgf20 or Fgf8) expression dynamics during X. laevis tadpole (stage 51) tail (C) or hindlimb bud (D) regeneration at 0, 1, 2, 5 dpa (days post amputation). The geometric mean of expression of two reference housekeeping genes: ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) and elongation factor 1alpa (EF-1alpha) was used for normalization of the target genes expression levels. (E) The expression of xRas-dva genes and regeneration marker genes in tadpole tails amputated in the refractory period (stage 46) at 1, 2, 5 dpa in comparison to 0 dpa. (F) qRT-PCR analysis of dRas-dva1, dRas-dva2 genes and Fgf20a, Igf2b markers expression pattern during the D. rerio fins regeneration on 1, 2 5 dpa in comparison to 0 dpa (the color of the fin on B correspond to the color of columns representing the gene expression in respective fin on F). All graphs represent means of quantification using total RNA derived from three independent samples. The value of normalized PCR signal in the 0 dpa sample, harvested immediately after amputation, was taken as an arbitrary unit (a.u.) in each series. Data are represented as mean ± SD, t-test, p < 0,05 (asterisk).