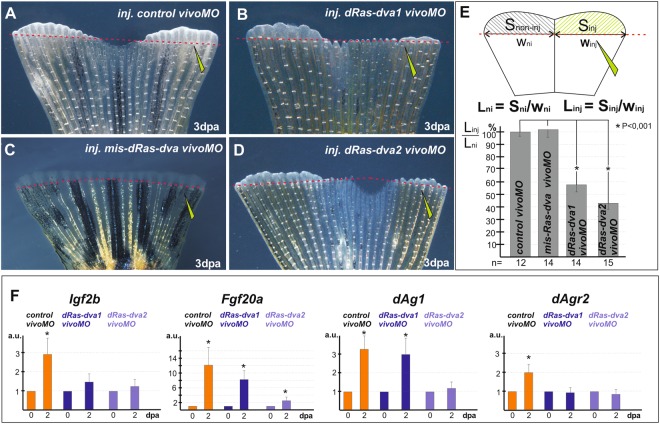
Figure 6.
Down-regulation of Ras-dva genes by vivo-morpholino oligonucleotides inhibits the D. rerio fin regeneration. (A–D) Transmitted light images of regenerating D. rerio caudal fins injected in the right half by control vivoMO (A), dRas-dva1 vivoMO (B), mis-dRas-dva1 vivoMO (C) or dRas-dva2 vivoMO (D) at 3 dpa. Red dashed line indicates amputation level. Distal is upside, dorsal is to the left. Scale bar 200 µm. (E) Regeneration efficiency is calculated as normalized area of regenerated part of the caudal fin at 3 dpa injected by vivoMO divided by the normalized area of regenerated part that was not injected. Resulting values were taken as a percentage of the value obtained for control vivoMO. The scheme demonstrates how normalized length value <L> was calculated. S – square mean, W-width mean, ni- non-injected part, inj-injected part. Error bars indicate SD. Statistical significance was determined with two-tailed t-test, the results are statistically significant, p < 0,001 (asterisk). (F) qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of early regeneration marker genes Igf2b and Fgf20a, as well as Agr genes, dAg1 and dAgr2, during the regeneration process (at 0 and 2 dpa) in the D. rerio caudal fins injected with control, dRas-dva1 or dRas-dva2 vivoMO. The scheme of experiment is the same as described in Fig. 2A. The value of normalized PCR signal in the 0 dpa sample, harvested immediately after amputation, was taken as an arbitrary unit (a.u.) in each series. Dpa - days post amputation. Error bars indicate SD, t-test, p < 0.05 (asterisk).