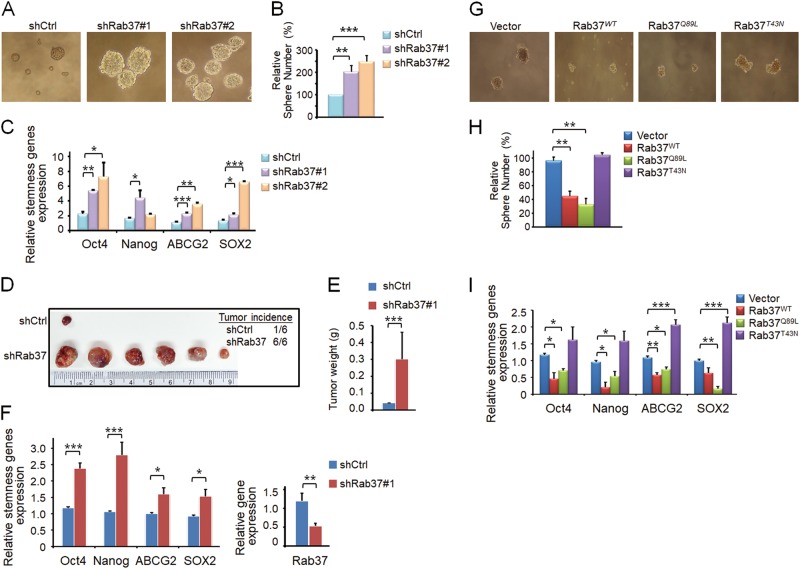
Fig. 1. Rab37 downregulation promotes lung cancer sphere formation ability in vitro and enhances tumor initiation ability in vivo.
a and b Rab37 knockdown (shRab37#1 or shRab37#2) promoted sphere-forming ability in H460 lung cancer cells. The representative sphere images (a) and sphere number (b) are shown. Spheres were counted after 7 days of incubation. The sphere number of each group was normalized to the sh-control (shCtrl) group. c RT-qPCR analysis of stemness-related genes in sphere cells derived from shCtrl, shRab37#1 or shRab37#2. Data were normalized to the shCtrl group. d–f Rab37 knockdown enhanced tumor initiation ability in vivo. The xenograft tumors were collected from BALB/c nude mice injected subcutaneously with 500 sphere-derived shCtrl or shRab37#1 H460 cells. The tumor incidence of each group is shown (Upper right) (d). The tumor weight was significantly increased in shRab37 group (e). RT-qPCR analysis of stemness genes (Left) and Rab37 gene (Right) in xenograft tissues derived from H460 cells (f). g and h Rab37WT or Rab37Q89L overexpression inhibited lung cancer sphere-forming ability in H1299 cells. The representative sphere images (g) and sphere number (h) are shown. i RT-qPCR analysis of stemness gene expression in H1299 spheres. Data were normalized to vector group. Data are mean ± SEM; N = 3 for cell-based study; N = 6 for animal study. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001 (Student’s t test)