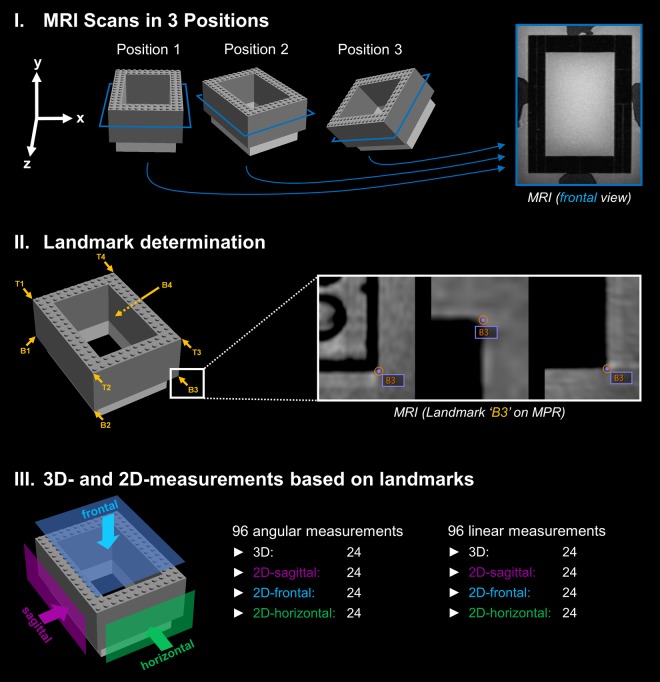
Figure 1.
Workflow for analyzing the accuracy of the applied MRI technique. I For accuracy measurements, a cuboid-shaped Lego phantom (127.8 mm × 95.8 mm × 48.0 mm) was scanned on a 3 Tesla MRI system using a high-resolution 3D sequence. The phantom was placed in a plastic box filled with water and contrast agent before it was scanned in three positions (normal alignment, rotated, rotated and lifted). An exemplary MR image in frontal orientation (according to the blue section planes on the phantom graphics) is shown on the right side. II For each phantom position, the 4 vertices on the top (T1–T4) and the 4 vertices on the bottom (B1–B4) were determined as landmarks on multiplanar reconstructions (MPR) using DICOM Imaging Software (Osirix v.7.0.3). III Based on the landmarks’ coordinates, a total of 96 angles and 96 distances were calculated for each phantom position using a customized software tool.