Figure 2.
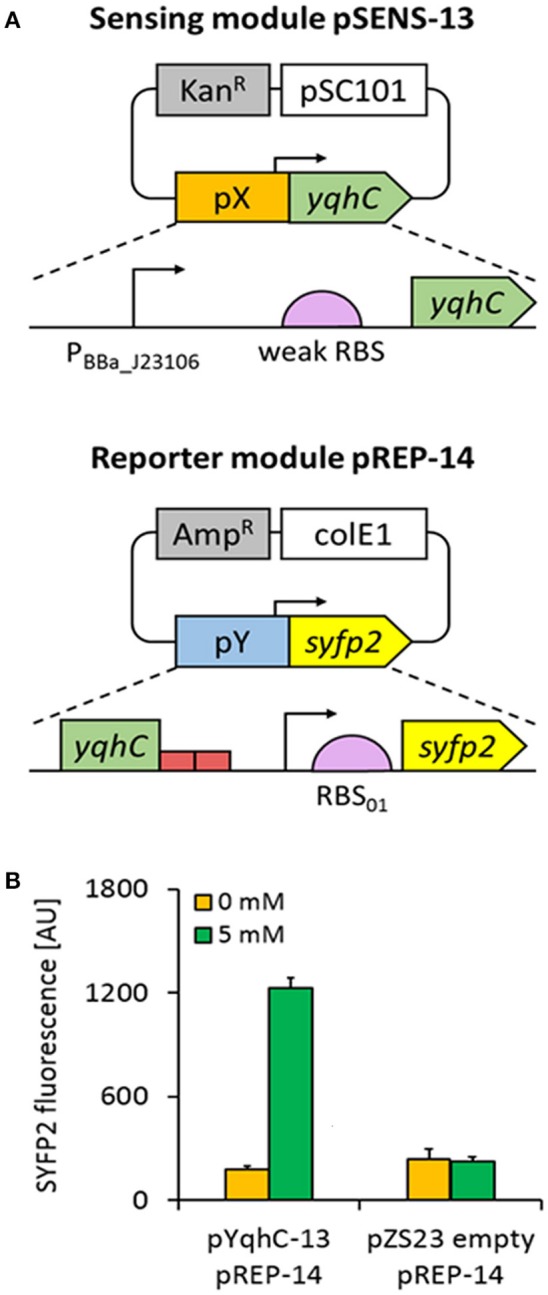
Design of the YqhC-based aldehyde sensor. (A) The sensing module pSENS-13 consists of a low-copy plasmid in which yqhC is under control of a medium-strength constitutive promoter (PBBa_J23106) and a weak ribosome binding site. The reporter module pREP-14 was built by fusing the syfp2 reporter gene (preceded by a strong RBS) to the YqhC cognate promoter in a high-copy vector. The 5′-UTR regions containing regulatory elements responsible by transcription of yqhC and reporter genes were named pX and pY, respectively. In each module, the antibiotic resistance marker and origin of replication is shown (gray and white boxes, respectively). (B) Fluorescence variation upon aldehyde exposure of engineered E. coli strain co-transformed with pSENS-13 and pREP-14. In a control experiment, the host strain was transformed with pZS23 and pREP-14. All strains are derived from the host strain CF30 (E. coli MG1655 Δsad ΔyqhD). Cells were cultivated in M9 mineral medium containing 20 g L−1 glucose and incubated for 4 h with 5 mM glycolaldehyde when OD600 reached ~0.6. SYFP2 fluorescence was calculated using cytometry data based on geometric mean. The reported values represent the mean ± S.D (n ≥ 2).
