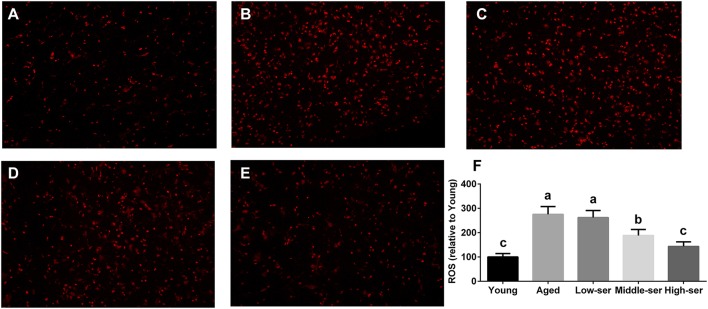
Figure 3.
Effects of long-term l-serine administration on the ROS content in aging mice. Representative images of ROS in mice from the Young (A), Aged (B), Low-ser (C), Middle-ser (D), and High-ser (E) groups; (F) Relative ROS content. Aged, untreated control mice; Low-ser, mice supplemented with 0.1% (wt/vol) l-serine dissolved in the drinking water; Middle-ser, mice supplemented with 0.2% (wt/vol) l-serine dissolved in the drinking water; High-ser, mice supplemented with 0.5% (wt/vol) l-serine dissolved in the drinking water. Young, adult male mice at the age of 18 months. ROS, reactive oxygen species. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 4. a, b, cMeans of the bars with different letters were significantly different among groups (P < 0.05).