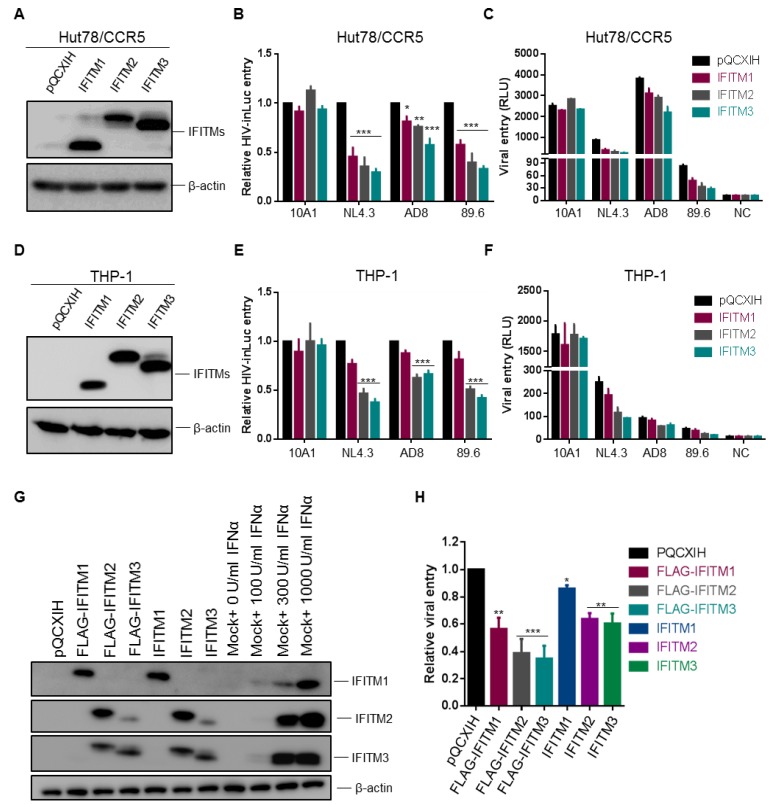
Figure 3.
Ectopic expression of IFITM proteins in CD4+ HuT78 and THP-1 cells equivalently inhibits entry of HIV-1 CXCR4 and CCR5 isolates. Experiments were performed the same as described for Figure 1 and Figure 2, except that HuT78 and THP-1 cells expressing individual IFITMs were used for infection. (A) IFITM1, 2, 3 expression levels in HuT78/CCR5 cells were examined by immunoblotting using an anti-FLAG antibody. (B,C) Infection of HIV-inGLuc bearing the Env of MLV 10A1, HIV-1 NL4.3, AD8 or 89.6, indicative of entry, in HuT78/CCR5 cells was shown. Relative entry efficiency was shown in (B) and absolute luciferase activities were plotted in (C). (D) IFITM1, 2, 3 expression levels in THP-1/CCR5 cells were examined by immunoblotting using an anti-FLAG antibody. (E,F) Infection of HIV-inGLuc bearing the Env of MLV 10A1, HIV-1 NL4.3, AD8 or 89.6, indicative of entry, in THP-1/CCR5 cells was presented. Relative entry efficiency was shown in (E) and absolute luciferase activities were plotted in (F). (G) Expression of FLAG-tagged and untagged wildtype (WT) IFITMs in SupT1 cells, as well as their comparisons with endogenous IFITMs in SupT1 cells induced by IFNα2b treatment (0, 100, 300 and 1000 U/mL). β-actin served as loading control. (H) Effect of FLAG-tagged and WT IFITMs on HIV-1 NL4.3 inGLuc infection in SupT1 cells determined by gaussia luciferase activities 48 h after infection. Data are mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.