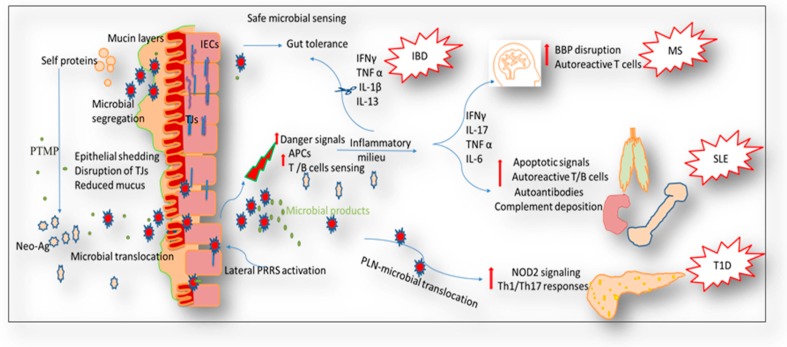
Figure 2.
Possible mechanisms of how a leaky gut leads to autoimmunity. Breakdown of the integrity of the intestinal mucosa is associated with microbial dysbiosis. This could result in epigenetic changes of both self-protein and pattern recognition receptor (PRR) sensing. Increased danger signals following microbial dysbiosis provoke immunogenic cell responses, consequently upregulating different pro-inflammatory cytokines levels such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)α, IFNγ, IL-1, IL-17, IL-6, and IL-13. These inflammatory niches are associated with different pathologies including IBD, MS, SLE, and T1D.