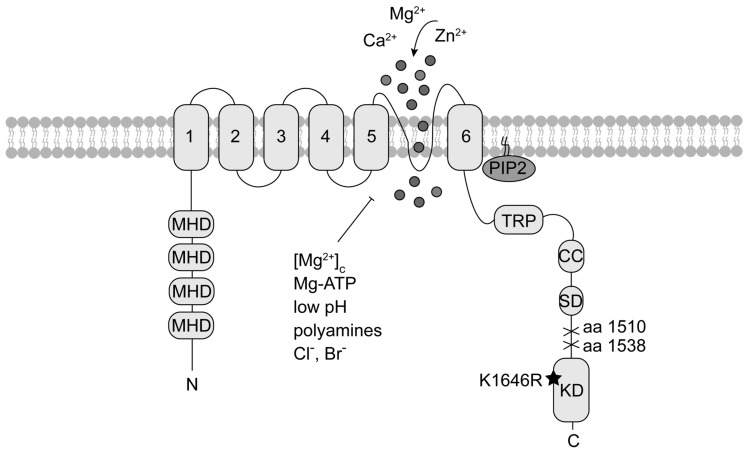
Figure 1.
TRPM7 topology. Each TRPM7 protein consists of six transmembrane segments (1 to 6) with the channel pore located between segment 5 and 6. Within the N-terminus are melastatin homology domains (MHD), characteristic for TRPM family members. The cytoplasmic C-terminus contains a transient receptor potential domain (TRP), a coiled-coil domain (CC) and a kinase substrate domain (SD) upstream the atypical α-type serine/threonine protein kinase domain (KD). Mutation at the catalytic side of the kinase (K1646R) abolishes kinase activity without affecting current activity. Deletion of the KD at different amino acids (aa) results in either enhanced or reduced current activity. The black star indicates the location of the point mutation, crosses mark the kinase deletion. TRPM7 is negatively regulated by depletion of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), physiologic free cytosolic magnesium concentrations [Mg2+]c, Mg-ATP, polyamines, low pH and chloride (Cl−) and bromide (Br−) concentrations.