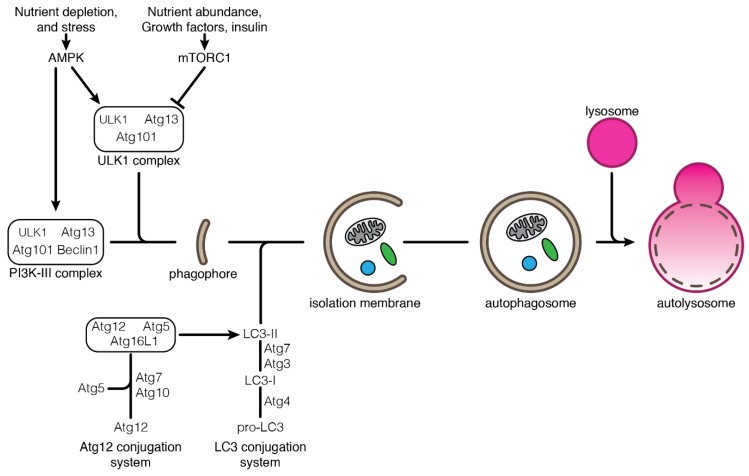
Figure 1.
An overview of the macroautophagy process. Initiation of autophagy is under the control of sensor pathways that can sense the availability of nutrients, growth factors, insulin or other stresses. The main regulators of autophagy are AMPK (AMP-activated kinase) and mTORC1 (mTOR complex (1) which act as autophagy activator and inhibitor, respectively. AMPK and mTORC1 regulate the activation of the ULK1 complex which, together with the PI3K-Ш complex, initiates the autophagosome formation. The formation of an autophagosome starts with the generation of a phagophore which elongates into an isolation membrane where the cargos to be degraded are gathered. The enclosure of the isolation membrane forms a double-membraned autophagosome that matures and eventually fuses with the lysosome, forming an autolysosome where lysosomal hydrolases degrade its content. The Atg12 and LC3 conjugation systems are essential for the autophagy process and formation of the autophagosome. The Atg12 conjugation system consists in the formation of the Atg12-Atg5-Atg16L1 complex that then promotes the conjugation of LC3; pro-LC3 is cleaved by Atg4 (LC3-I) which is then conjugated with phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) (LC3-II) before being anchored to the nascent autophagosomal membrane.