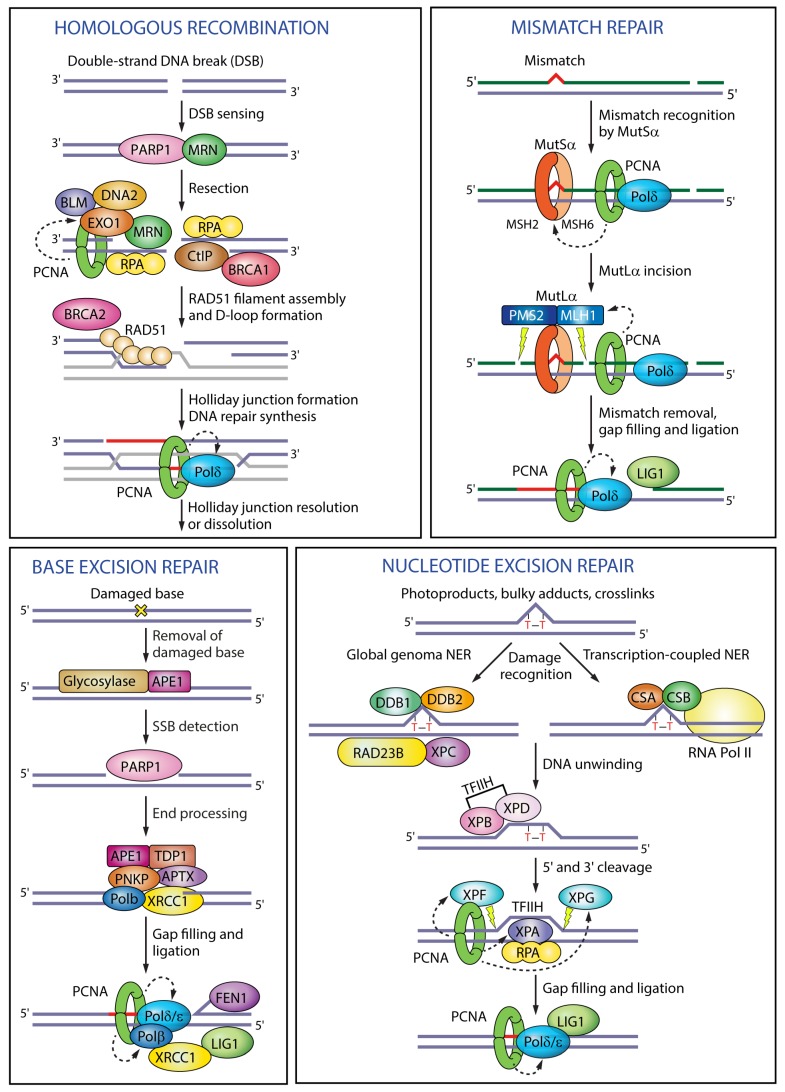
Figure 3.
Functions of PCNA in different DNA repair pathways. In homologous recombination PCNA enhances the processivity of the exonuclease EXO1 during end resection and of Pol δ during DNA repair synthesis. In mismatch repair, PCNA interacts with MutSα to recognize the mismatch, activates the endonuclease activity of MutLα to excise the mismatch, and recruits polymerase δ for DNA repair synthesis. In base excision repair, PCNA recruits polymerases β, δ or ε to displace the damaged base into a flap intermediate. In nucleotide excision repair PCNA interacts with the scaffold protein XPA, activates the endonuclease XPF, targets XPG for degradation and recruits polymerase δ to fill in the gap. Black dashed arrows indicate PCNA targets in different pathways. RPA (replication protein A); CtIP (CtBP-interacting protein); MSH2 (MutS homologue 2); MSH6 (MutS homologue 6); MLH1 (MutL homologue 1); PMS2 (PMS1 homologue 2); APE1 (apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1); TDP1 (tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1); PNKP (polynucleotide kinase 3′-phosphatase); APTX (aprataxin); XRCC1 (X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 1); DDB1 (DNA damage-binding protein 1); DDB2 (DNA damage-binding protein 2); RAD23B (RAD23 homologue B); XPC (Xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group C); CSA (Cockayne syndrome group A); CSB (Cockayne syndrome group B); TFIIH (transcription factor II H); XPB (Xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group B); XPD (Xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group D).